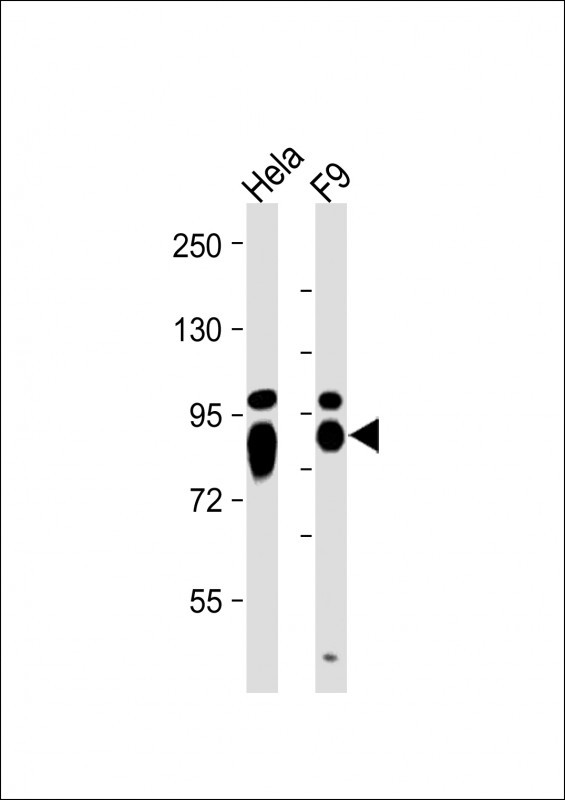
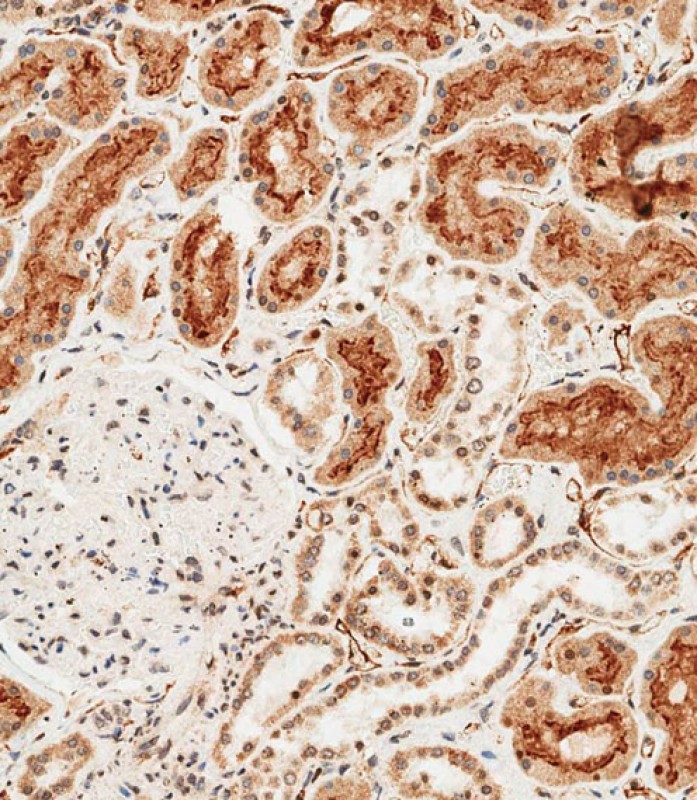
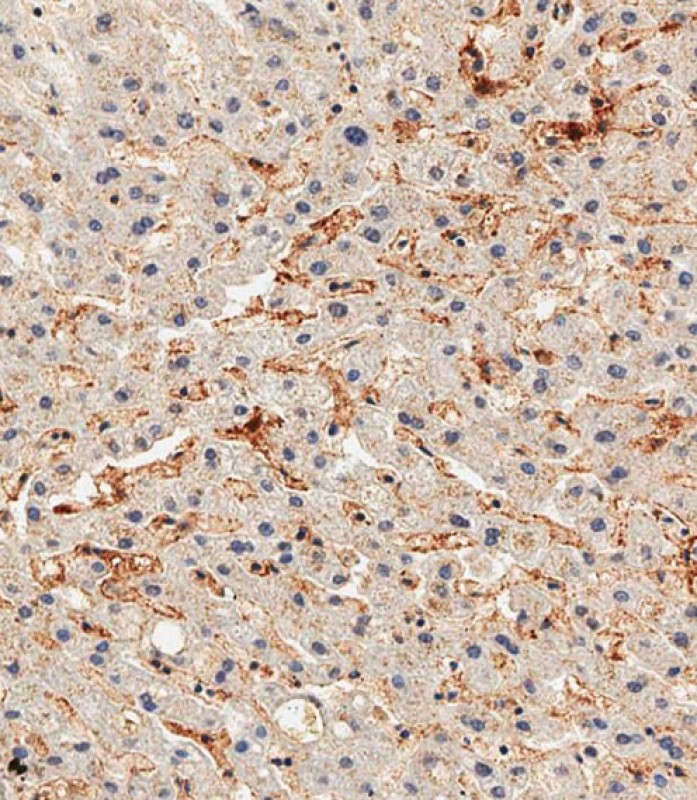
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme, AP-TNAP, TNSALP, Alkaline phosphatase liver/bone/kidney isozyme, ALPL |
| Entrez GeneID | 249 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This ALPL antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 217-246 amino acids from the Central region of human ALPL. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于ALPL抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容概述:
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) in patients with hypophosphatasia*
**作者**:Watanabe et al. (2021)
**摘要**:该研究在低磷酸酯酶症(HPP)患者血清中检测到针对组织非特异性碱性磷酸酶(TNSALP/ALPL)的自身抗体(IgG型),并发现抗体滴度与骨骼矿化缺陷的严重程度相关,提示自身免疫反应可能加剧疾病进展。
2. **文献名称**:*ALPL autoantibodies as a novel biomarker in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Smith et al. (2020)
**摘要**:研究发现结直肠癌患者血清中ALPL自身抗体的水平显著升高,且与肿瘤分期和转移风险相关,表明ALPL抗体可能作为潜在的癌症诊断或预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*Inhibition of TNSALP activity by monoclonal anti-ALPL antibodies: Implications for enzyme replacement therapy*
**作者**:Johnson et al. (2018)
**摘要**:通过开发靶向ALPL的单克隆抗体,研究证实这些抗体可特异性抑制TNSALP的酶活性,为低磷酸酯酶症的病理机制及酶替代疗法的免疫副作用提供了新见解。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)中的具体信息。若需进一步精准检索,建议结合关键词“ALPL antibody”和“hypophosphatasia”或“autoimmunity”筛选近年研究。
ALPL antibodies target tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP), an enzyme encoded by the *ALPL* gene. TNSALP is critical in mineralization processes, particularly in bones and teeth, by hydrolyzing inorganic pyrophosphate (a mineralization inhibitor) and phosphate esters to promote hydroxyapatite formation. It is also expressed in the liver, kidneys, and placenta. ALPL mutations cause hypophosphatasia (HPP), a rare metabolic disorder characterized by defective bone mineralization, dental abnormalities, and variable systemic complications depending on disease severity.
ALPL antibodies are utilized in research and diagnostics to detect TNSALP expression or activity. In clinical settings, they help diagnose HPP by identifying reduced enzyme activity or aberrant protein structure. Research applications include studying skeletal development, mineralization pathways, and TNSALP's role in pathologies like vascular calcification or cancer. Some antibodies inhibit enzymatic activity, aiding mechanistic studies, while others serve as detection tools in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, Western blot) or immunohistochemistry to localize TNSALP in tissues.
Therapeutic ALPL-targeting antibodies are under exploration, particularly for managing HPP. However, most treatments focus on enzyme replacement therapy (e.g., asfotase alfa) rather than immunomodulation. Commercial ALPL antibodies vary in specificity, with some distinguishing between tissue-specific isoforms. Challenges include ensuring cross-reactivity across species in preclinical models and distinguishing functional versus inactive enzyme forms. Overall, ALPL antibodies remain vital tools for unraveling the enzyme's biological roles and advancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for related disorders.
×