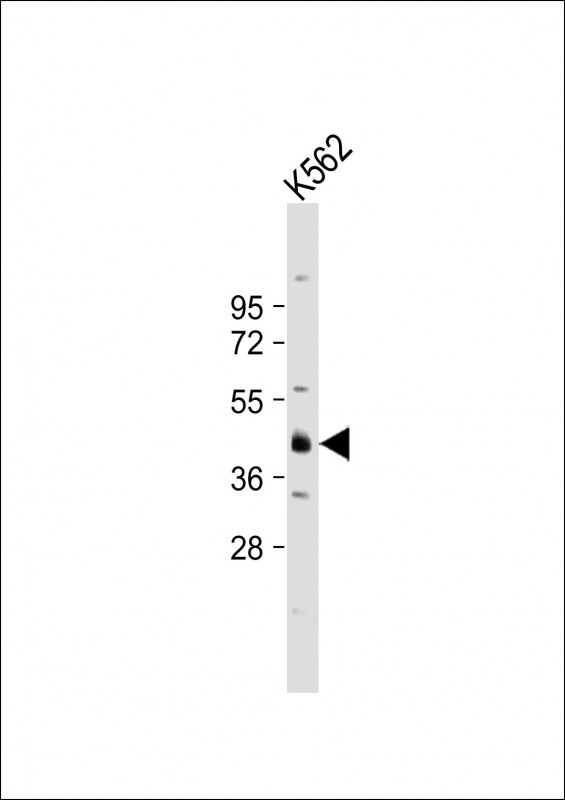
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
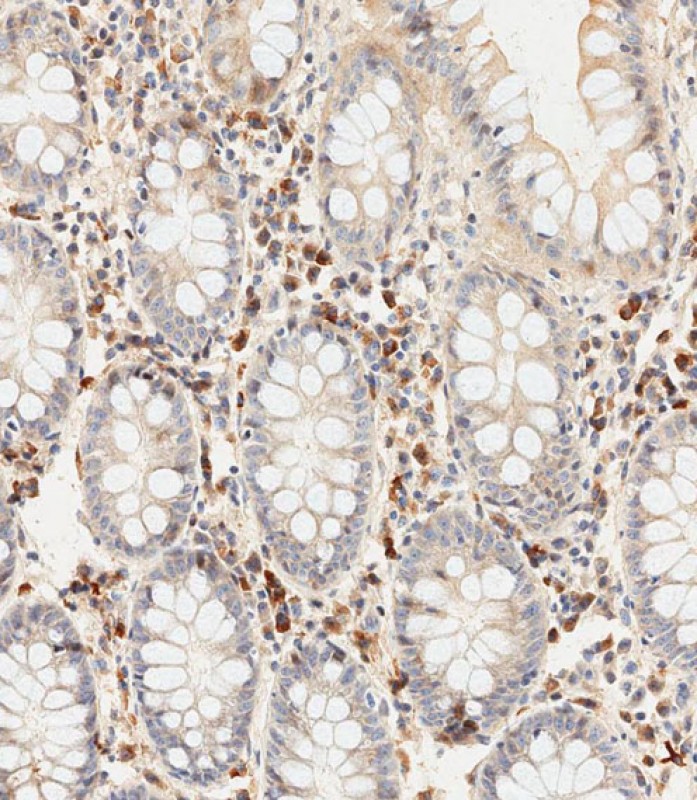
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ubiquitin thioesterase OTU1, DUBA-8, HIV-1-induced protease 7, HIN-7, HsHIN7, OTU domain-containing protein 2, YOD1, DUBA8, HIN7, OTUD2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55432 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This YOD1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 319-347 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human YOD1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于YOD1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*YOD1/TRAF6 association regulates p62-mediated oxidative stress-induced autophagosome accumulation*
**作者**:Schaeffer, V. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了YOD1通过与TRAF6相互作用调控细胞自噬的机制,利用YOD1抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)实验,证实YOD1在氧化应激条件下促进自噬小体聚集,并影响p62依赖的蛋白降解通路。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Deubiquitinating enzyme YOD1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) through interaction with Derlin-1*
**作者**:Ernst, R. et al.
**摘要**:作者通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用YOD1抗体)证明,YOD1通过结合Derlin-1参与内质网相关降解(ERAD),调控错误折叠蛋白的逆向转运和泛素化修饰,影响细胞应激反应的存活能力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*YOD1 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for high-risk neuroblastoma*
**作者**:Tsuchiya, M. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用YOD1抗体检测肿瘤组织中YOD1的表达水平,发现抑制YOD1的去泛素化酶活性可诱导神经母细胞瘤细胞凋亡,并增强化疗敏感性,提示YOD1作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**:*The deubiquitinase YOD1 modulates α-synuclein pathology through regulation of lysosomal degradation*
**作者**:Ji, C. et al.
**摘要**:该文献通过免疫组化(使用YOD1抗体)分析帕金森病模型,发现YOD1通过调控溶酶体功能影响α-突触核蛋白的降解,其活性缺失导致毒性蛋白聚集,加剧神经退行性病变。
---
以上研究均涉及YOD1抗体的实验应用(如蛋白检测、定位或互作分析),并围绕YOD1在疾病机制中的功能展开。
YOD1. also known as OTUD2. is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) belonging to the ovarian tumor (OTU) protease family. It plays a critical role in regulating protein homeostasis, particularly within the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. YOD1 is involved in the quality control of misfolded proteins by facilitating their retrotranslocation from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen to the cytosol for proteasomal degradation. It exhibits both ubiquitin-binding and deubiquitinating activities, enabling it to edit ubiquitin chains on substrate proteins or associated chaperones, thereby influencing their fate. YOD1's function is tightly linked to the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and its dysregulation has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and immune disorders.
YOD1-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. These antibodies are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate YOD1's role in cellular stress responses, protein degradation, and disease mechanisms. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes in human YOD1. with validation in multiple species. Recent studies highlight YOD1's dual role in ERAD—promoting substrate dislocation while preventing excessive ubiquitination—making its antibodies crucial for dissecting these complex regulatory mechanisms. Research using YOD1 antibodies has also explored its potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in conditions involving proteotoxic stress or aberrant ubiquitination pathways.
×