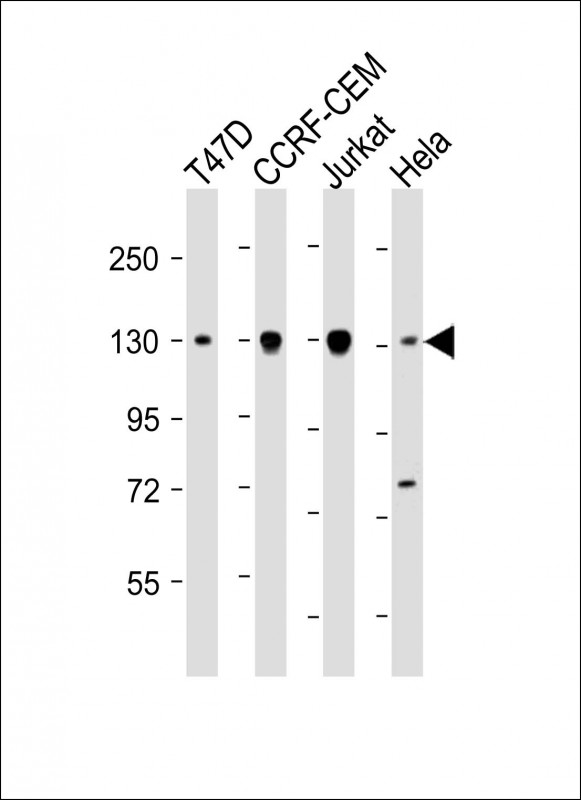
| WB | 1/2000-1/4000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A, Dnmt3a, 2.1.1.37, DNA methyltransferase HsaIIIA, DNA MTase HsaIIIA, M.HsaIIIA, DNMT3A |
| Entrez GeneID | 1788 |
| WB Predicted band size | 101.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This Dnmt3a antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein of human Dnmt3a. |
+ +
以下是关于Dnmt3a抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **《DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development》**
- **作者**:Okano, M., Bell, D.W., Haber, D.A., Li, E.
- **摘要**:该研究通过生成Dnmt3a和Dnmt3b的特异性抗体,揭示了这两种酶在胚胎发育过程中介导DNA从头甲基化的关键作用,并证明其缺失会导致小鼠胚胎致死。
2. **《De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase activities in mouse embryonic stem cells》**
- **作者**:Lei, H., Oh, S.P., Okano, M., Jüttermann, R., Goss, K.A., Jaenisch, R.
- **摘要**:文章利用Dnmt3a抗体分析小鼠胚胎干细胞中DNA甲基转移酶活性,发现Dnmt3a与Dnmt3b共同调控早期发育阶段的甲基化模式,为表观遗传机制提供了实验依据。
3. **《Dnmt3a mutations in acute myeloid leukemia》**
- **作者**:Ley, T.J., Ding, L., Walter, M.J., et al.
- **摘要**:该研究通过免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫组化(IHC)技术,结合Dnmt3a抗体,发现急性髓系白血病患者中Dnmt3a基因突变导致其蛋白功能异常,与疾病进展和预后相关。
4. **《Dnmt3a regulates neuronal survival and cognition in the mammalian brain》**
- **作者**:Gulmez Karaca, K., Kupke, J., Brito, D.V.C., et al.
- **摘要**:研究使用Dnmt3a特异性抗体检测小鼠脑组织,证明Dnmt3a通过调控突触可塑性和神经基因表达,影响学习记忆能力及神经元存活。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时需核对原文准确性。)
The Dnmt3a antibody is a critical tool in epigenetic research, specifically targeting DNA methyltransferase 3A (Dnmt3a), a key enzyme responsible for establishing de novo DNA methylation patterns during development. Dnmt3a, along with its homolog Dnmt3b, catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups to cytosine residues in CpG dinucleotides, a process essential for gene regulation, genomic imprinting, and X-chromosome inactivation. Unlike Dnmt1. which maintains methylation during DNA replication, Dnmt3a acts during early embryogenesis and cellular differentiation, shaping cell-specific epigenetic landscapes.
Antibodies against Dnmt3a are widely used to study its expression, localization, and functional roles in both normal and pathological contexts. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the exploration of Dnmt3a’s involvement in stem cell differentiation, cancer (e.g., leukemia, where mutations are common), and neurodevelopmental disorders. Researchers also utilize these antibodies to investigate interactions with co-factors like Dnmt3L or histone modifications that regulate methylation activity.
Commercial Dnmt3a antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal regulatory or C-terminal catalytic domains. Validation often includes knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Challenges include cross-reactivity with Dnmt3b due to structural similarities, emphasizing the need for rigorous validation. Overall, Dnmt3a antibodies remain indispensable for dissecting the enzyme’s role in epigenetic regulation and disease mechanisms.
×