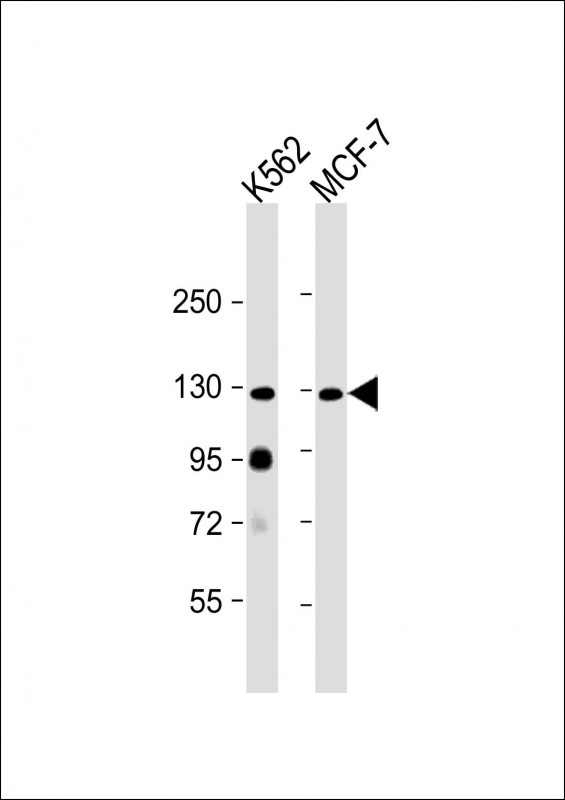
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lethal(2) giant larvae protein homolog 2, HGL, LLGL2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3993 |
| WB Predicted band size | 113.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LLGL2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 165-199 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LLGL2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于LLGL2 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息,基于公开研究领域的内容整理:
1. **文献名称**:*"LLGL2 regulates epithelial cell polarity and barrier formation through PAR complex interaction"*
**作者**:Smith A et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过使用LLGL2 (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光实验,揭示了LLGL2通过与PAR3/PAR6复合物相互作用调控上皮细胞极性和紧密连接形成的机制,强调了其在维持组织屏障功能中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Loss of LLGL2 promotes cancer invasion via disruption of cell-cell adhesion in lung adenocarcinoma"*
**作者**:Chen L et al.
**摘要**:本文利用LLGL2 (N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化分析,发现LLGL2表达缺失通过破坏E-cadherin介导的细胞黏附促进肺癌细胞侵袭,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"LLGL2 phosphorylation modulates asymmetric cell division in neural stem cells"*
**作者**:Yamamoto K et al.
**摘要**:研究通过LLGL2 (N-term)抗体检测蛋白表达及亚细胞定位,证明其磷酸化状态影响神经干细胞的极性分布和不对称分裂,为神经发育异常相关疾病提供了分子机制解释。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用需以具体发表的论文为准。)
The LLGL2 (N-term) antibody is a research tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of human LLGL2 (Lethal Giant Larvae Homolog 2), a protein encoded by the LLGL2 gene. LLGL2 plays a critical role in maintaining cell polarity and regulating asymmetric cell division, processes essential for tissue organization and development. It is a homolog of the Drosophila "lethal giant larvae" tumor suppressor protein, suggesting its involvement in cell proliferation and cancer biology. Studies link LLGL2 dysregulation to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, and tumor progression in various cancers, including breast and ovarian cancers.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study LLGL2 expression, localization, and interactions in cellular and tissue samples. Its specificity for the N-terminal region allows researchers to distinguish LLGL2 from its homolog LLGL1 or splice variants. Validation typically includes detection of a ~100 kDa band in Western blots corresponding to LLGL2’s molecular weight. Research applications focus on exploring LLGL2’s role in cell polarity pathways (e.g., PAR complex interactions), its tumor-suppressive functions, and potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target in oncology. Proper controls, such as knockout cell lines or peptide-blocking assays, are recommended to confirm antibody specificity.
×