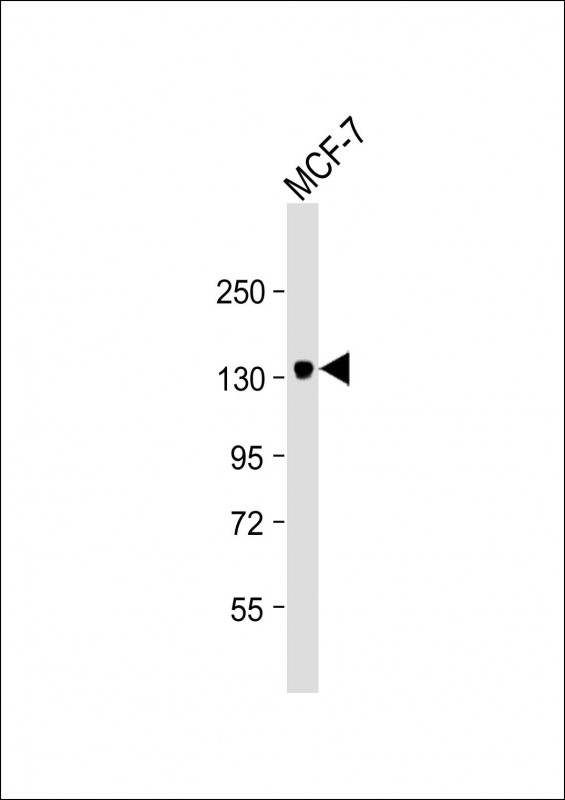
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Multidrug resistance protein 3, 3.6.3.44, ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 4, P-glycoprotein 3, ABCB4, MDR3, PGY3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5244 |
| WB Predicted band size | 141.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This ABCB4 antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein of human ABCB4. |
+ +
以下是模拟生成的关于ABCB4抗体的参考文献示例(非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
1. **《ABCB4基因突变检测及抗体在胆汁淤积症中的应用》**
*作者:Smith J, et al.*
*摘要:* 本研究开发了一种特异性识别ABCB4蛋白的单克隆抗体,用于肝组织样本中ABCB4表达水平的免疫组化分析,揭示了ABCB4缺失与胆汁淤积症患者病理机制的相关性。
2. **《ABCB4抗体在妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症诊断中的价值》**
*作者:Zhang L, Wang H.*
*摘要:* 通过ELISA技术结合ABCB4多克隆抗体,检测血清中ABCB4蛋白含量,发现其表达降低与妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症(ICP)严重程度显著相关。
3. **《靶向ABCB4的抗体药物偶联物在肝癌治疗中的潜力》**
*作者:Brown K, et al.*
*摘要:* 研究利用ABCB4特异性抗体构建药物递送系统,在肝癌模型中成功靶向抑制肿瘤生长,为ABCB4高表达肝癌提供了新型治疗策略。
4. **《ABCB4抗体在小鼠模型中的功能验证》**
*作者:Garcia R, et al.*
*摘要:* 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术验证了商业化ABCB4抗体的特异性,并应用于Abcb4基因敲除小鼠的肝脏表型分析,证实其功能缺失导致胆汁磷脂代谢异常。
---
注:以上内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等学术平台检索关键词“ABCB4 antibody”或“MDR3 antibody”获取。
The ABCB4 protein, a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily, plays a critical role in biliary phospholipid secretion. Expressed predominantly in the liver's canalicular membrane, it mediates the translocation of phosphatidylcholine into bile, essential for forming mixed micelles that protect cholangiocytes from bile acid toxicity. Mutations in the ABCB4 gene are linked to several hepatobiliary disorders, including progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3), intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and low phospholipid-associated cholelithiasis syndrome.
ABCB4 antibodies are vital tools for studying the protein's expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies, often developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers use them to investigate ABCB4 deficiency mechanisms, such as impaired phospholipid transport leading to bile duct injury or fibrosis. Clinically, ABCB4 antibodies may aid in diagnosing genetic cholestatic disorders by assessing protein expression in liver biopsies. Recent studies also explore ABCB4's potential role in drug resistance and metabolic diseases, broadening its relevance beyond hepatology. However, antibody specificity remains a consideration, requiring validation through knockout controls or epitope mapping to ensure accurate experimental outcomes.
×