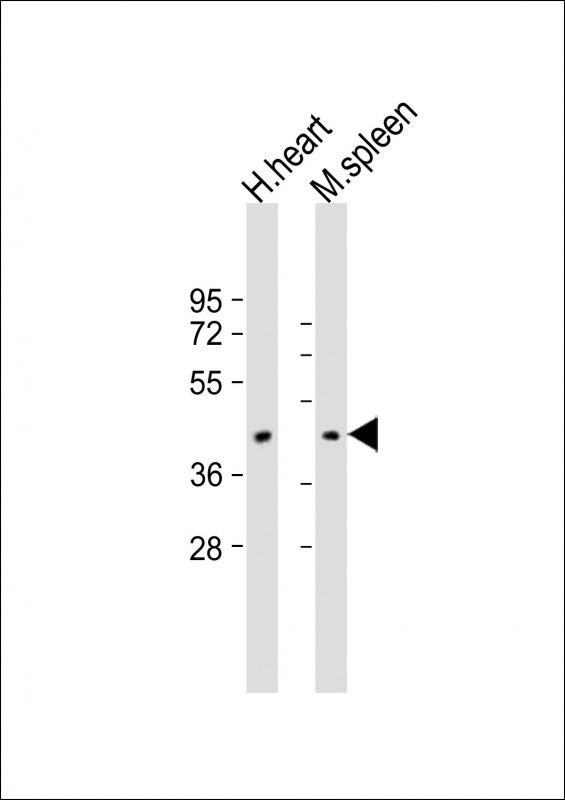
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
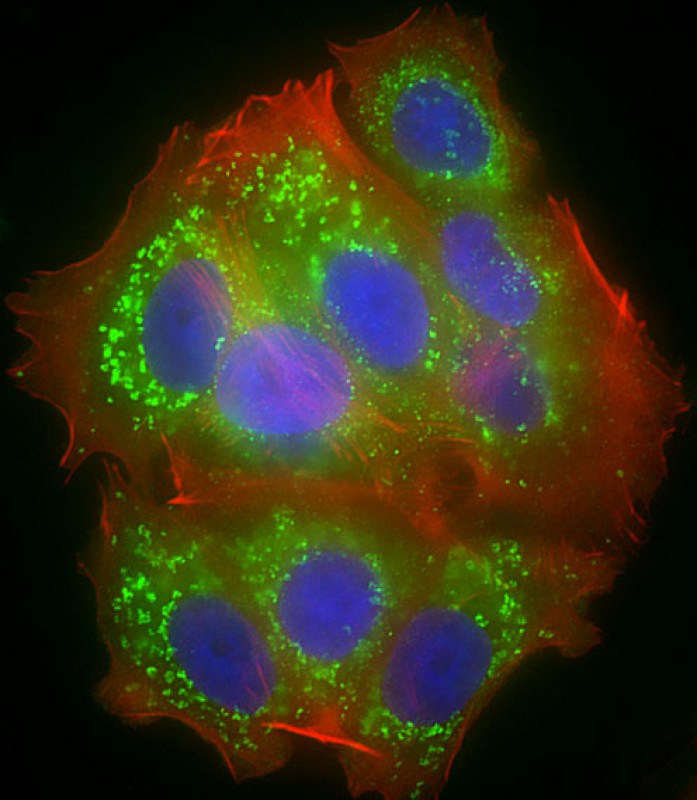
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1, Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide I, MT-CO1, COI, COXI, MTCO1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4512 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This COXI antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 195-224 amino acids of human COXI. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于细胞色素C氧化酶亚基I(COX I/MT-CO1)抗体的参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mitochondrial COX I as a Biomarker in Neurodegenerative Diseases*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用COX I特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织,发现COX I表达水平显著降低,提示线粒体功能障碍与神经退行性病变相关。
2. **文献名称**:*COX I Antibody Validation for Mitochondrial Complex IV Studies*
**作者**:Lee H, Patel R.
**摘要**:文章系统验证了多种商业COX I抗体的特异性,确认其在检测哺乳动物细胞线粒体呼吸链复合物IV中的可靠性,为氧化磷酸化研究提供实验依据。
3. **文献名称**:*COX I Expression in Cancer: Implications for Therapeutic Targeting*
**作者**:Garcia M, et al.
**摘要**:通过COX I抗体标记,发现多种实体瘤中线粒体COX I蛋白异常高表达,提示其可能成为癌症代谢重编程的治疗靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Role of COX I in Zebrafish Cardiac Development*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用COX I抗体进行斑马鱼胚胎免疫荧光染色,证实COX I缺失导致心脏发育缺陷,强调线粒体能量代谢在器官形成中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:若您需要真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“COX I antibody”或“Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I antibody”获取最新研究。
COXI (Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit I) antibodies are essential tools in studying mitochondrial function and cellular energy metabolism. Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), also known as Complex IV, is the terminal enzyme in the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), responsible for catalyzing the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to molecular oxygen, a critical step in ATP synthesis. COXI, encoded by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), is one of the three core catalytic subunits (COXI, COXII, COXIII) forming the functional core of the enzyme.
COXI antibodies are widely used to detect and quantify COX expression, serving as markers for mitochondrial content and integrity. They are pivotal in research on mitochondrial diseases (e.g., Leigh syndrome, mitochondrial encephalomyopathies), where COX deficiency is a common feature. Additionally, these antibodies aid in investigating conditions linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s), cancer, and aging.
In experimental settings, COXI antibodies are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess tissue-specific mitochondrial activity or damage. Their specificity helps distinguish between nuclear DNA- and mtDNA-encoded proteins, offering insights into mitochondrial biogenesis and gene expression regulation. Recent studies also utilize COXI antibodies to explore metabolic adaptations in hypoxia, oxidative stress, and cancer cell energetics.
Overall, COXI antibodies remain indispensable for advancing our understanding of mitochondrial biology and its implications in health and disease.
×