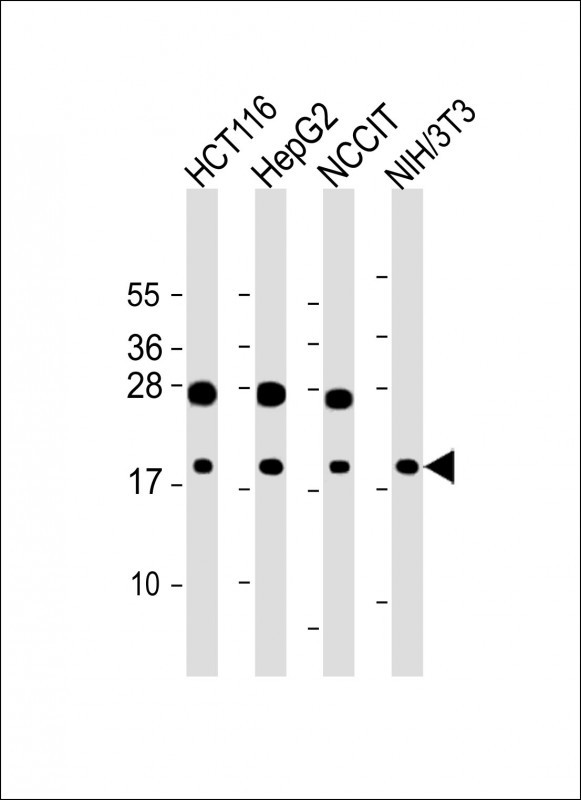
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | High mobility group protein HMGI-C, High mobility group AT-hook protein 2, HMGA2, HMGIC |
| Entrez GeneID | 8091 |
| WB Predicted band size | 11.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This HMGA2 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 15-49 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human HMGA2. |
+ +
以下是关于HMGA2 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简明信息:
1. **文献名称**: *HMGA2 phosphorylation by CK2 regulates its interaction with DNA*
**作者**: Pierantoni GM, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用HMGA2 N端特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和质谱分析,揭示了CK2激酶对HMGA2 N端结构域的磷酸化修饰,并证明此修饰影响其与DNA的结合能力,进而调控靶基因表达。
2. **文献名称**: *HMGA2 promotes EMT in pancreatic cancer via transcriptional activation of Snail*
**作者**: Li XY, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验(使用HMGA2 N端抗体),研究证实HMGA2在胰腺癌中过表达并通过激活Snail转录促进上皮-间质转化(EMT),从而驱动肿瘤侵袭转移。
3. **文献名称**: *Role of HMGA2 in maintaining cancer stem cell properties*
**作者**: Morishita A, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献使用N端特异性抗体检测HMGA2在结肠癌干细胞中的表达,发现HMGA2通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路维持干细胞特性,敲低HMGA2显著抑制肿瘤球形成能力。
4. **文献名称**: *HMGA2 antibody validation for immunohistochemical analysis in clinical samples*
**作者**: Rogalla P, et al.
**摘要**: 研究系统验证了HMGA2 N端抗体在石蜡包埋组织中的特异性,证实其在乳腺癌和肺癌中的核定位表达与患者预后不良相关,为临床病理检测提供可靠工具。
注:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“HMGA2 N-terminal antibody”或“HMGA2 antibody validation”检索最新论文。
The HMGA2 (N-term) antibody is designed to detect the N-terminal region of the High Mobility Group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) protein, a non-histone chromatin-associated protein involved in regulating gene expression, chromatin structure, and cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. HMGA2 contains three conserved AT-hook DNA-binding domains, primarily localized in the N-terminal region, which facilitate interactions with AT-rich DNA sequences to modulate transcriptional activity. This antibody specifically targets epitopes within or near these functional domains, making it valuable for studying HMGA2's role in development, stem cell maintenance, and cancer biology.
HMGA2 is overexpressed in various malignancies, including breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers, where it promotes tumor progression, metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Conversely, HMGA2 loss is linked to growth restriction syndromes. The HMGA2 (N-term) antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. Researchers also employ it in chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to explore HMGA2-DNA interactions. Due to HMGA2's low molecular weight (~12 kDa), careful validation is required to distinguish it from cross-reactivity with similar proteins like HMGA1. Its applications span basic research, biomarker studies, and therapeutic target validation in oncology.
×