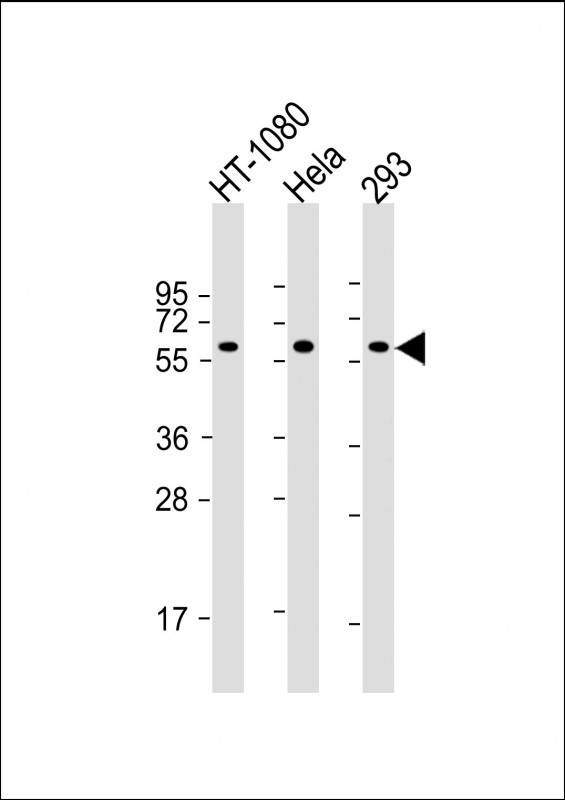
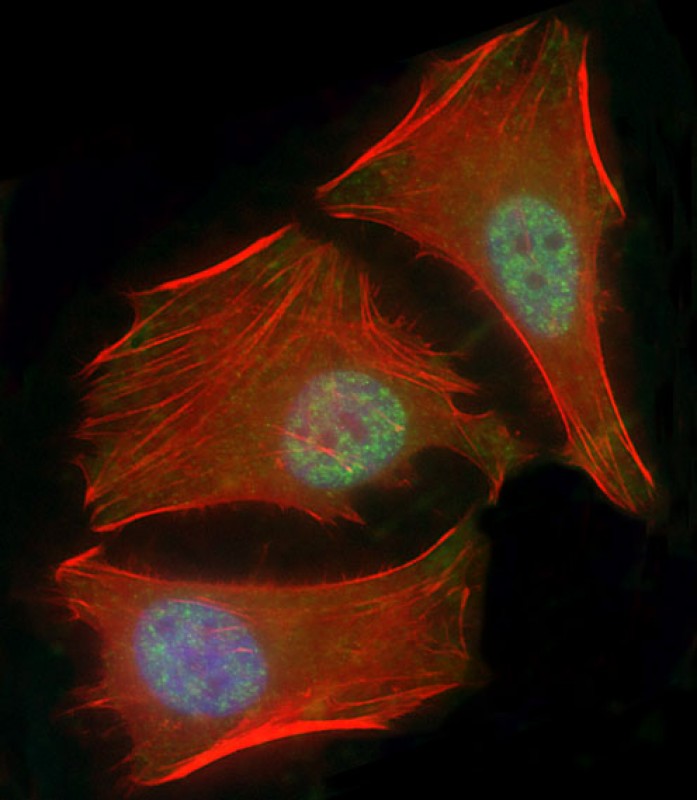
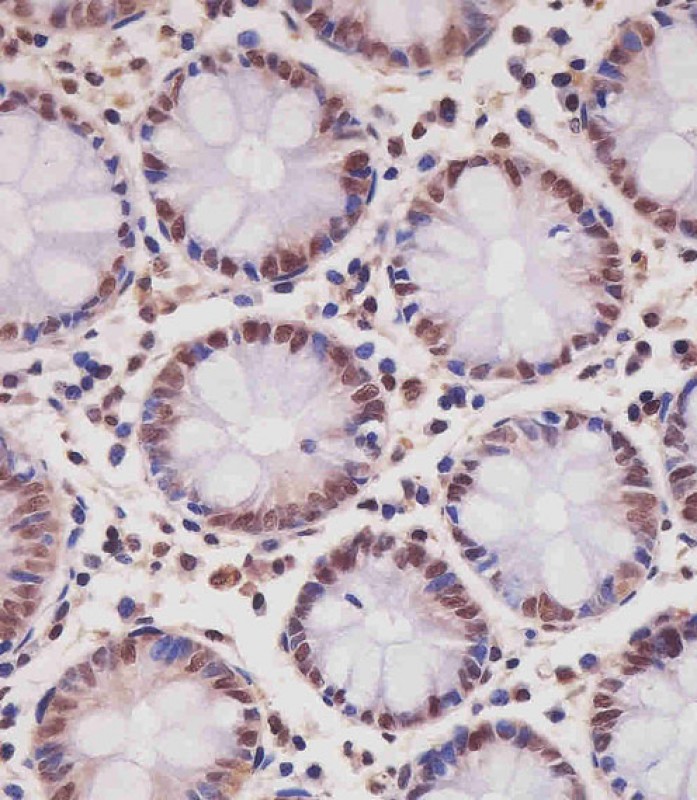
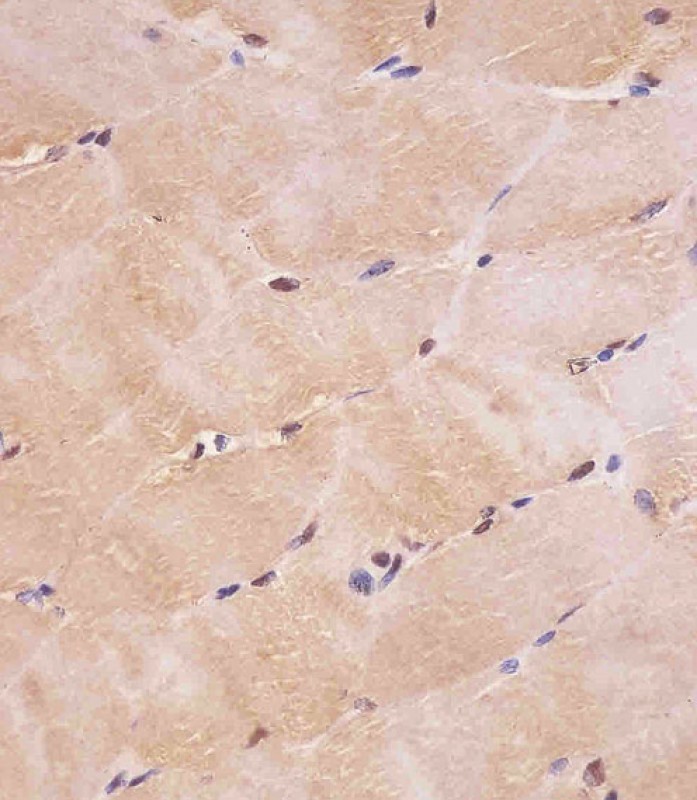
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1, MAD homolog 1, Mothers against DPP homolog 1, JV4-1, Mad-related protein 1, SMAD family member 1, SMAD 1, Smad1, hSMAD1, Transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein 1, BSP-1, SMAD1, BSP1, MADH1, MADR1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4086 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SMAD1 antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein between 20-330 amino acids from human SMAD1. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SMAD1抗体的代表性文献(虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **"Specific detection of phosphorylated SMAD1 using a monoclonal antibody in BMP signaling studies"**
*Author: Liu Y, et al.*
摘要:本研究开发了一种高特异性单克隆抗体,可特异性识别磷酸化的SMAD1蛋白(p-SMAD1),并验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用。该抗体成功应用于BMP信号通路激活的定量分析。
---
2. **"SMAD1 antibody validation in developmental biology models"**
*Author: Thompson R, et al.*
摘要:通过基因敲除小鼠模型和siRNA敲低实验,验证了多种商业SMAD1抗体的特异性。研究发现,抗体在胚胎组织中的染色结果与SMAD1基因表达谱高度一致,强调了抗体选择对发育机制研究的重要性。
---
3. **"Cross-reactivity analysis of SMAD family antibodies reveals subtype-specific signaling dynamics"**
*Author: Gupta S, et al.*
摘要:系统性评估了SMAD1抗体与其他SMAD家族蛋白(如SMAD5/8)的交叉反应性,结合质谱数据证实其特异性。该抗体被用于揭示SMAD1在癌症细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)中的独特作用。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索以下关键词:
`SMAD1 antibody specificity validation`、`SMAD1 BMP signaling`、`SMAD1 immunohistochemistry`
SMAD1 is a critical intracellular signaling molecule belonging to the SMAD family, which mediates transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily signaling, particularly bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathways. As a receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD), SMAD1 is activated through phosphorylation by BMP type I receptors upon ligand binding. This triggers its association with SMAD4 (Co-SMAD) and subsequent translocation to the nucleus, where the complex regulates transcription of target genes involved in embryonic development, cell differentiation, apoptosis, and tissue homeostasis.
SMAD1 antibodies are essential tools for studying BMP signaling dynamics. These antibodies specifically detect SMAD1 protein in various applications, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Researchers frequently use them to investigate SMAD1 activation status (phosphorylated vs. non-phosphorylated forms), subcellular localization, and protein-protein interactions. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against epitopes in the N-terminal (MH1 domain) or C-terminal (MH2 domain) regions, with some targeting phosphorylation sites (e.g., Ser463/465).
Dysregulation of SMAD1 has been implicated in developmental disorders, cancer progression, and fibrotic diseases. SMAD1 antibodies thus play a vital role in both basic research and clinical studies, enabling the characterization of BMP pathway alterations in disease models and therapeutic interventions. Validation parameters for these antibodies often include knockout cell line verification and species cross-reactivity testing (human, mouse, rat). Careful antibody selection is crucial due to potential cross-reactivity with other SMAD family members (e.g., SMAD5. SMAD8/9) in some commercial products.
×