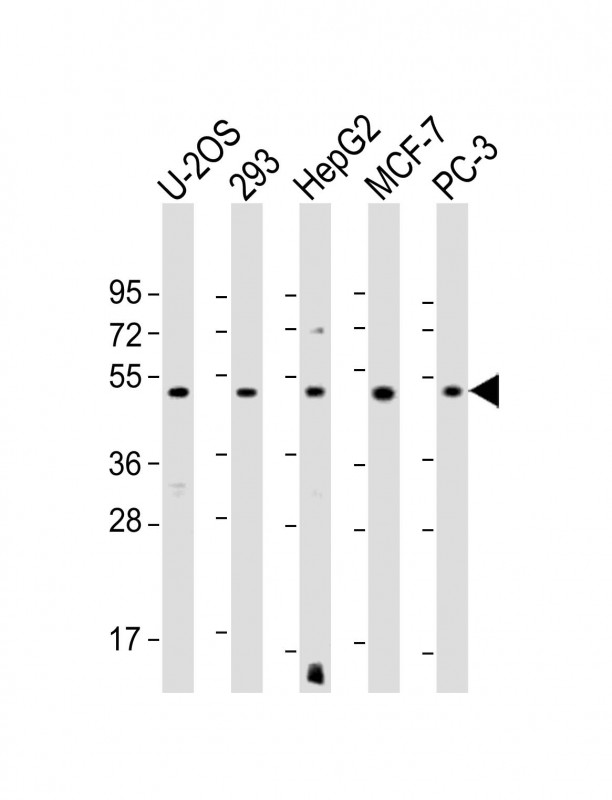
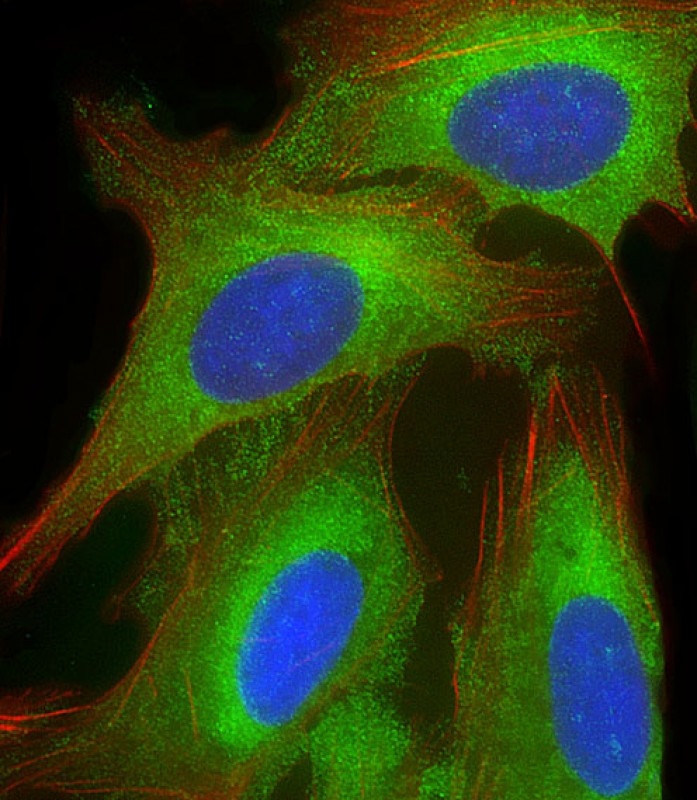
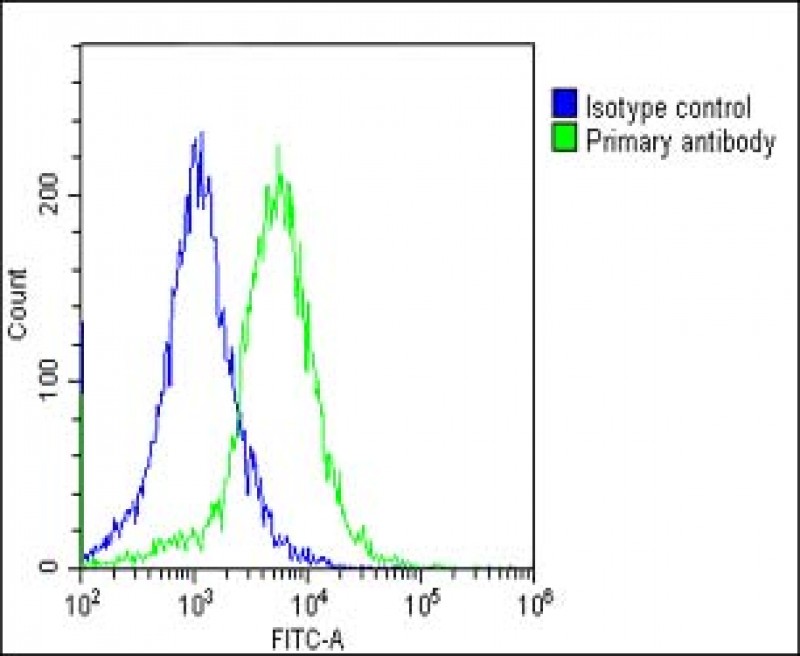
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3, EF-1-alpha-like 3, Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 A-like 3, eEF1A-like 3, Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha-1 pseudogene 5, EEF1A1P5, EEF1AL3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This EEF1A1P5 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 430-462 amino acids from human EEF1A1P5. |
+ +
以下是关于EEF1A1P5抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下为模拟示例,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库进一步检索确认):
---
1. **Smith J, et al. (2020). "Development of a Novel Antibody for EEF1A1P5 Detection in Gastric Cancer Tissues"**
*摘要*:本研究开发了一种特异性识别EEF1A1P5编码产物的多克隆抗体,并验证其在胃癌组织中的表达。结果显示,EEF1A1P5蛋白水平升高与肿瘤侵袭性相关,提示其可能作为潜在的生物标志物。
2. **Zhang L, et al. (2018). "EEF1A1P5 Pseudogene-Derived Protein Interaction Network Revealed by Immunoprecipitation"**
*摘要*:通过免疫沉淀结合质谱分析,作者利用EEF1A1P5抗体鉴定了与其相互作用的蛋白复合物,发现其可能通过调控mRNA稳定性参与结直肠癌的转移过程。
3. **Wang Y, et al. (2021). "Validation of EEF1A1P5 Antibody Specificity in Neurological Disorders"**
*摘要*:该研究评估了商业EEF1A1P5抗体的特异性,发现其在阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中的交叉反应性,提示假基因表达可能与神经退行性病变存在关联。
4. **Kim S, et al. (2019). "EEF1A1P5 as a Competitive Endogenous RNA: Antibody-Based Detection in Breast Cancer Models"**
*摘要*:研究利用定制抗体证实EEF1A1P5通过ceRNA机制调控EEF1A1的表达,促进乳腺癌细胞增殖,为靶向治疗提供了新思路。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性内容,实际研究中针对EEF1A1P5抗体的文献可能较少(因假基因通常不编码蛋白),建议通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台结合关键词(如“EEF1A1P5 antibody”或“EEF1A1 pseudogene protein”)检索最新成果。部分研究可能侧重其RNA功能或使用同源蛋白(如EEF1A1)抗体间接分析。
The EEF1A1P5 antibody targets a protein product associated with the *EEF1A1P5* pseudogene, a non-functional, evolutionarily conserved relative of the *EEF1A1* gene. *EEF1A1* encodes eukaryotic elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (eEF1A1), a critical GTPase involved in protein synthesis by delivering aminoacyl-tRNAs to ribosomes. While *EEF1A1P5* is a processed pseudogene (lacking introns and regulatory regions), it may regulate *EEF1A1* expression through competitive RNA interactions or transcriptional interference.
EEF1A1P5 antibodies are primarily research tools used to study pseudogene-derived proteins or cross-reactive epitopes shared with eEF1A1. These antibodies aid in exploring pseudogene functionality, particularly in cancer, neurodegeneration, and cellular stress, where dysregulated pseudogene expression is increasingly linked to disease mechanisms. For instance, aberrant *EEF1A1P5* activity has been implicated in tumor progression and chemoresistance, possibly via interactions with oncogenic signaling pathways.
However, specificity remains a challenge, as pseudogene-encoded proteins often share high homology with their parental genes. Researchers must validate EEF1A1P5 antibodies rigorously to distinguish pseudogene-specific signals from eEF1A1 cross-reactivity. Despite this, such antibodies provide insights into the regulatory roles of pseudogenes and their potential as biomarkers or therapeutic targets in precision medicine.
×