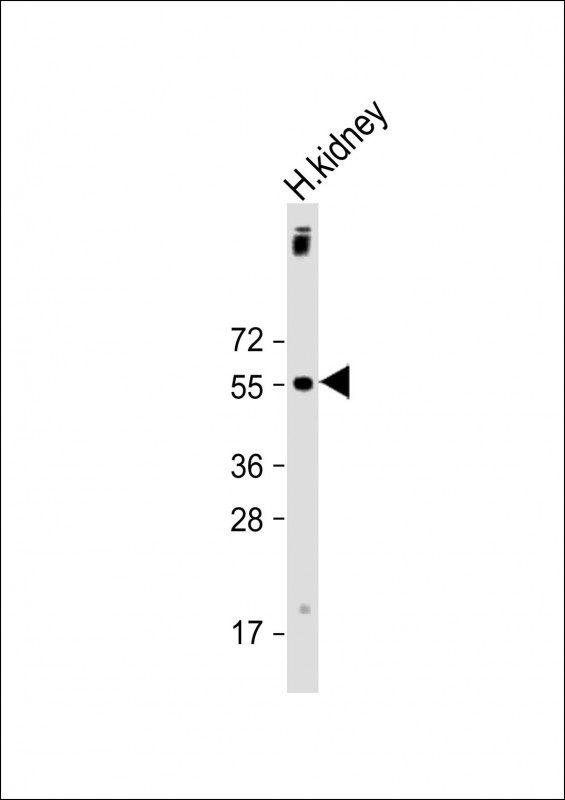
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-9, UDPGT 1-9, UGT1*9, UGT1-09, UGT1.9, 2.4.1.17, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-I, UGT-1I, UGT1I, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A9, lugP4, UGT1A9, GNT1, UGT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54600 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This UGT1A9 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 408-439 amino acids from the human UGT1A9. |
+ +
以下是关于UGT1A9抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Characterization of UGT1A9 monoclonal antibody for specificity and application in human tissue analysis*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发并验证了一种高特异性的UGT1A9单克隆抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化证实其在人肝、肾组织中的选择性表达,并用于评估UGT1A9蛋白水平的个体差异。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Role of UGT1A9 in drug glucuronidation: Insights from antibody-based inhibition studies*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 利用UGT1A9特异性抗体进行体外抑制实验,揭示UGT1A9对多种药物(如SN-38、丙戊酸)的葡萄糖醛酸化代谢贡献,为药物相互作用研究提供工具。
---
3. **文献名称**: *UGT1A9 genetic polymorphism and protein expression in colorectal cancer: An immunohistochemical analysis*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗体验证UGT1A9在结直肠癌组织中的表达下调,并探讨其与患者生存率及化疗反应的相关性,提示UGT1A9可能作为潜在生物标志物。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需查询真实数据库(如PubMed)获取准确信息。如需具体文献,建议使用关键词“UGT1A9 antibody”或“UGT1A9 immunolocalization”检索相关学术平台。
The UGT1A9 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A9 (UGT1A9) enzyme, a member of the UGT superfamily responsible for phase II drug metabolism and detoxification. UGT1A9 is primarily expressed in the liver, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract, where it catalyzes the glucuronidation of endogenous compounds (e.g., steroids, bilirubin) and exogenous substances, including drugs (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antivirals) and environmental toxins. This enzymatic process enhances their water solubility, facilitating excretion.
UGT1A9 antibodies are developed using immunogens such as recombinant proteins or synthetic peptides corresponding to specific regions of the UGT1A9 protein. They are widely employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and ELISA to detect UGT1A9 expression, localization, and regulation in tissues or cell lines. These antibodies help investigate interindividual variability in drug metabolism linked to genetic polymorphisms (e.g., UGT1A9*3), which can influence enzyme activity and drug response.
Research using UGT1A9 antibodies has clinical relevance, as altered UGT1A9 activity impacts drug efficacy and toxicity. For example, reduced glucuronidation may lead to adverse effects from drugs like mycophenolate mofetil or irinotecan. Validating antibody specificity via knockout controls is critical, as UGT isoforms share high sequence homology. Reliable UGT1A9 antibodies thus support studies on drug-drug interactions, personalized medicine, and disease mechanisms.
×