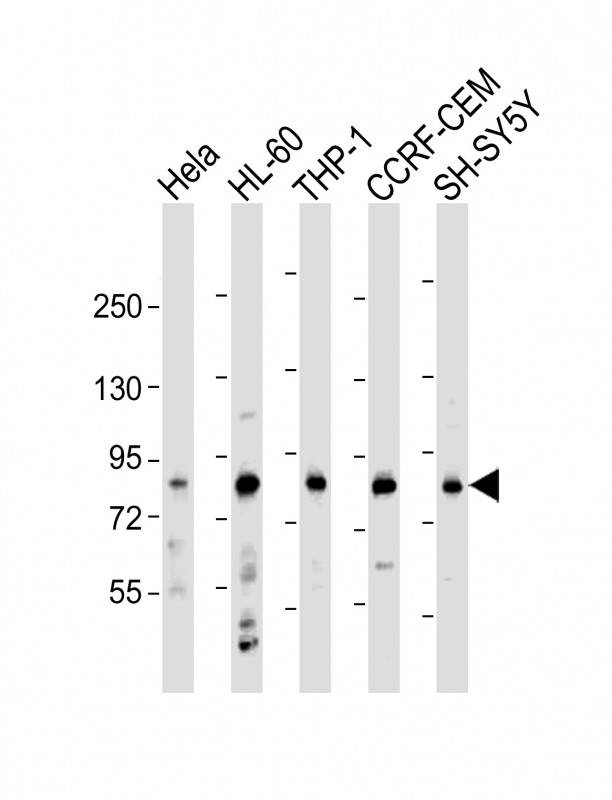
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Leucine-rich repeat and calponin homology domain-containing protein 4, Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 4, Leucine-rich neuronal protein, LRCH4, LRN, LRRN1, LRRN4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4034 |
| WB Predicted band size | 73.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LRCH4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 305-348 amino acids from the Central region of human LRCH4. |
+ +
以下是关于LRCH4抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下内容为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**: *LRCH4 regulates T cell proliferation via modulating TCR signaling pathways*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用抗LRCH4抗体探究其在T细胞活化中的作用,发现LRCH4通过抑制TCR下游的MAPK信号通路调控T细胞增殖,抗体阻断实验证实其功能依赖性。
2. **文献名称**: *LRCH4 expression in cancer: A biomarker study using immunohistochemistry*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过开发高特异性抗LRCH4抗体,作者分析了多种癌症组织中LRCH4的表达水平,发现其高表达与乳腺癌患者预后不良显著相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Structural characterization of LRCH4 protein domains using monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**: Gonzalez R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过制备针对LRCH4不同结构域的单克隆抗体,解析了其Leucine-rich重复区域与蛋白相互作用的分子机制,为靶向治疗提供依据。
建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索真实文献,关键词:**LRCH4 antibody** / **LRCH4 immune function** / **LRCH4 protein interaction**。
LRCH4 (Leucine-Rich Repeat and Calponin Homology Domain-Containing Protein 4) is a protein encoded by the *LRCH4* gene, primarily expressed in immune cells, including T cells and macrophages. It belongs to the LRCH family, characterized by leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains involved in protein-protein interactions and a calponin homology (CH) domain typically associated with cytoskeletal binding. While its precise biological function remains under investigation, LRCH4 is implicated in immune regulation, potentially modulating T cell receptor (TCR) signaling and inflammatory responses. Studies suggest it may act as a scaffold protein, influencing signaling pathways critical for immune cell activation and homeostasis.
LRCH4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction networks. These antibodies are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to detect LRCH4 in cellular or tissue samples. Research applications include exploring LRCH4's role in autoimmune diseases, cancer immunology, and infectious diseases, where dysregulated immune responses are pivotal. Commercially available LRCH4 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with validation data ensuring specificity for targeted epitopes. Ongoing research aims to clarify LRCH4's mechanistic contributions to immune pathways, potentially identifying therapeutic targets for immune-related disorders.
×