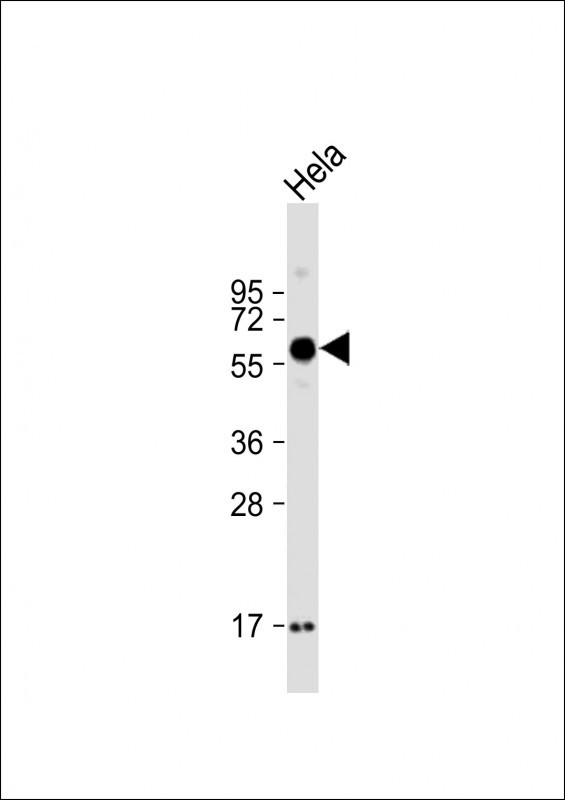
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1, Secreted modular calcium-binding protein 1, SMOC-1, SMOC1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 64093 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This SMOC1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 284-313 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human SMOC1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SMOC1抗体的3篇参考文献及简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*SMOC1 regulates apoptosis in colorectal cancer through the BMP4/Smad1/XIAP axis*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用SMOC1特异性抗体进行免疫组化和Western blot分析,发现SMOC1通过调控BMP4/Smad1信号通路影响结直肠癌细胞凋亡,并揭示了其与XIAP蛋白的关联性,提示SMOC1可能作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*SMOC1 mutations cause ocular anterior segment dysgenesis and microphthalmia*
**作者**:Okada M, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光技术结合SMOC1抗体,研究证实SMOC1基因突变导致小鼠胚胎眼发育异常,其蛋白在角膜和晶状体前体细胞中高表达,为小眼症及前段发育异常提供了分子机制解释。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Extracellular matrix protein SMOC1 modulates TGF-β signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts*
**作者**:Li H, et al.
**摘要**:利用SMOC1抗体进行组织微阵列分析,发现肿瘤间质中SMOC1高表达与TGF-β通路活化相关,提示其在癌相关成纤维细胞中通过调控ECM重塑促进肿瘤进展。
---
如需具体DOI或补充文献可进一步说明。
SMOC1 (SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1) is a secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) protein belonging to the SPARC family, characterized by calcium-binding domains and follistatin-like regions. It plays roles in tissue development, angiogenesis, and cell-matrix interactions by modulating growth factor signaling (e.g., BMP, Wnt) and ECM remodeling. SMOC1 is expressed in various tissues, including the eye, kidney, and cardiovascular system, and is implicated in developmental processes such as embryogenesis and organogenesis. Dysregulation of SMOC1 has been linked to pathologies like cancer, fibrosis, and ocular disorders (e.g., microphthalmia).
SMOC1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying the protein's expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate SMOC1's role in disease mechanisms or developmental biology. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within SMOC1's conserved domains. Validation data (e.g., knockout controls, peptide blocking) ensure specificity. Research utilizing SMOC1 antibodies has highlighted its potential as a biomarker in tumors and fibrotic diseases, as well as its regulatory effects on ECM dynamics and cellular signaling pathways.
×