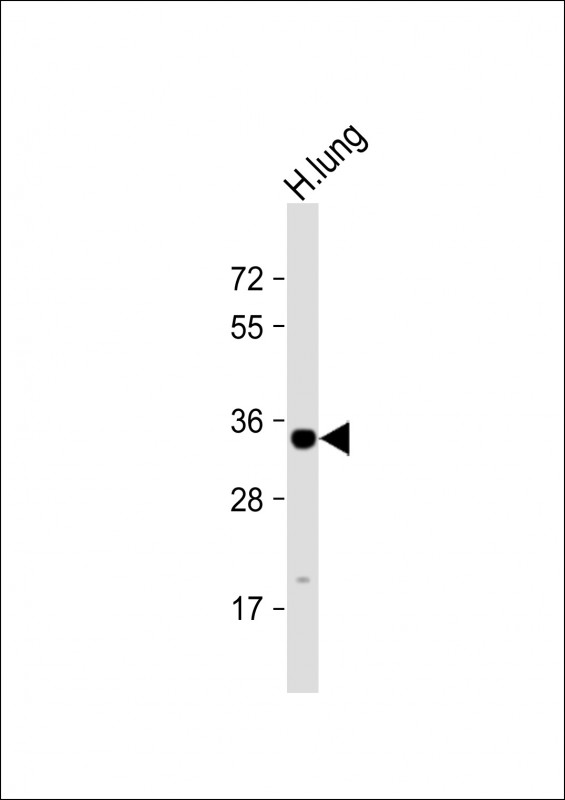

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-4, Transducin beta chain 4, GNB4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 59345 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GNB4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 109-138 amino acids from the Central region of human GNB4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GNB4抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*GNB4 mutations cause an autosomal-recessive multisystem syndrome with cardiac and neurological involvement*
**作者**:Lupo V. et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了GNB4基因突变与神经发育障碍和心脏异常的关联。通过免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫荧光实验,研究者利用特异性GNB4抗体证实了突变导致蛋白质表达量显著下降,提示GNB4在神经和心脏组织中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Characterization of Gβ4 as a potential biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种新型GNB4单克隆抗体,验证了其在肝癌组织中的高特异性。通过免疫组化(IHC)分析发现,GNB4在肝癌样本中异常高表达,提示其可能作为肝癌诊断或预后标志物的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*G-protein subunit beta-4 regulates axonal growth and synapse formation via the mTOR pathway*
**作者**:Kim S. et al.
**摘要**:本文通过体外神经元模型,使用GNB4抗体进行蛋白质定位和功能研究,发现GNB4通过调控mTOR信号通路影响轴突生长和突触形成,为神经退行性疾病的机制提供了新见解。
---
这些文献涵盖了GNB4抗体的应用场景(如疾病机制研究、诊断标志物开发)及实验方法(如Western blot、免疫组化),可供相关研究参考。如需具体文献链接或补充,可进一步说明。
The GNB4 antibody targets the G protein subunit beta 4 (GNB4), a member of the beta subunit family of heterotrimeric G proteins. These proteins play critical roles in intracellular signaling by coupling G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to downstream effectors. GNB4. specifically, forms part of the Gβγ complex and is involved in regulating diverse cellular processes, including neurotransmitter release, ion channel activity, and cell proliferation. Unlike other beta subunits (e.g., GNB1. GNB2), GNB4 exhibits tissue-specific expression, with higher levels observed in the nervous system, suggesting specialized roles in neuronal signaling.
Mutations in the GNB4 gene have been linked to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), a hereditary peripheral neuropathy, highlighting its importance in maintaining peripheral nerve function. Research using GNB4 antibodies has focused on elucidating its localization, expression patterns, and interactions within signaling pathways. These antibodies are essential tools for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, enabling the study of GNB4's role in health and disease. Recent studies also explore its potential involvement in cancer and neurodevelopmental disorders, underscoring its broader biomedical relevance. Validated GNB4 antibodies are crucial for ensuring specificity and reproducibility in experimental models, aiding in the development of targeted therapies for related conditions.
×