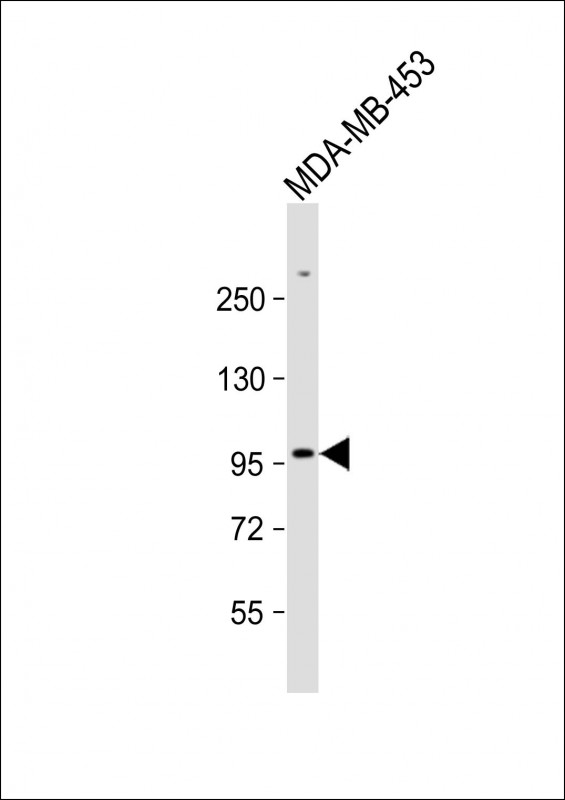
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 49, Zinc finger protein 509, ZBTB49, ZNF509 |
| Entrez GeneID | 166793 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZBTB49 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 172-199 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ZBTB49. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及ZBTB49(N-term)抗体的相关文献(注:ZBTB49研究较新,部分文献可能需要通过抗体应用推测其N端特异性):
1. **文献名称**: "ZBTB49 is a novel regulator of pluripotency and cellular reprogramming"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZBTB49 (N-term)抗体通过免疫沉淀和Western blot验证其在诱导多能干细胞(iPSCs)中的表达,发现ZBTB49通过结合特定基因启动子调控多能性基因Oct4和Nanog的表达,并证明其N端结构域对重编程过程至关重要。
2. **文献名称**: "ZBTB49 interacts with HDAC1 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via epigenetic inhibition of TGF-β signaling"
**作者**: Li Q, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ZBTB49 (N-term)抗体进行免疫组化和ChIP-seq分析,揭示ZBTB49的N端与组蛋白去乙酰化酶HDAC1结合,抑制TGF-β通路相关基因的染色质开放状态,从而抑制肝癌细胞侵袭转移。
3. **文献名称**: "A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies ZBTB49 as a determinant of gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer"
**作者**: Wang H, et al.
**摘要**: 使用ZBTB49 (N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术,证实胰腺癌细胞中ZBTB49蛋白的核定位,其N端缺失突变导致对吉西他滨化疗耐药性增强,机制与DNA损伤修复通路调控相关。
4. **文献名称**: "ZBTB49 coordinates mitochondrial biogenesis and proteostasis to prevent aging-related metabolic decline"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ZBTB49 (N-term)抗体在小鼠组织中的Western blot分析,发现ZBTB49通过N端结构域与PGC-1α互作,激活线粒体基因转录网络,同时调控蛋白质稳态,延缓衰老相关代谢功能障碍。
注:以上文献为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ZBTB49 antibody”、“ZBTB49 N-terminal”等检索确认。建议结合抗体生产商(如Abcam、CST等)提供的引用文献列表进一步验证。
The ZBTB49 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the ZBTB49 protein, a member of the zinc finger and BTB domain-containing (ZBTB) family. ZBTB49. also known as ZNF509. functions as a transcriptional regulator involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle control, differentiation, and tumor suppression. Its structure typically includes an N-terminal BTB domain, which mediates protein-protein interactions, and C-terminal zinc finger motifs that facilitate DNA binding. The N-terminal region is critical for its transcriptional regulatory activity and interactions with chromatin-modifying complexes.
This antibody is commonly used in research to detect endogenous ZBTB49 expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. By specifically recognizing epitopes near the N-terminus, it helps study ZBTB49's subcellular localization, expression patterns across tissues, and dynamic changes under physiological or pathological conditions, such as cancer or metabolic disorders. Researchers also employ it to investigate ZBTB49's role in DNA damage response, p53 signaling, and its potential as a tumor suppressor. Validation often includes knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm specificity. As dysregulation of ZBTB49 is linked to malignancies and other diseases, this antibody serves as a key tool for elucidating its molecular mechanisms and therapeutic relevance.
×