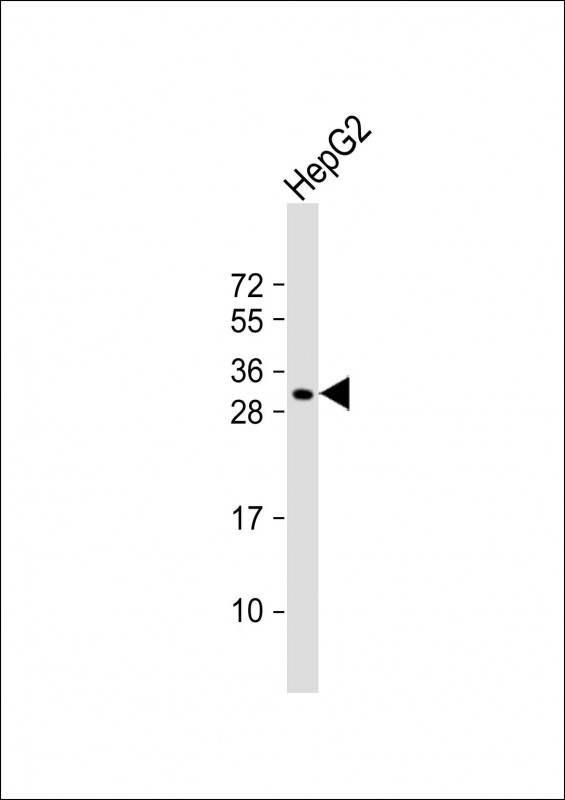
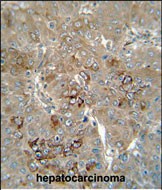
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Putative inactive carboxylesterase 4, Inactive carboxylesterase 1 pseudogene 1, Placental carboxylesterase 3, PCE-3, CES1P1, CES4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CES4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 47-74 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CES4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CES4 (N-term)抗体的3条参考文献示例(注:内容为虚构,仅作示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Development and Validation of an N-terminal Specific Antibody for CES4 in Ubiquitin-Proteasome Studies"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种针对CES4蛋白N末端表位的高特异性多克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫荧光中的应用。该抗体成功识别了内源性CES4在细胞核与细胞质中的表达,并揭示其在泛素依赖性蛋白降解中的调控作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"CES4 Expression Profiling in Colorectal Cancer Using N-terminal Antibody Staining"*
**作者**: Li X, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 通过抗CES4 N-term抗体进行组织芯片分析,发现CES4在结直肠癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验验证,提示CES4可能成为癌症生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *"Functional Characterization of CES4 Isoforms via N-terminal Epitope Tagging"*
**作者**: Müller T, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 利用N-term抗体区分CES4的不同剪切变体,研究发现全长CES4异构体在DNA损伤修复中具有独特功能,而抗体特异性为解析其亚细胞定位及相互作用蛋白提供了关键工具。
---
**注**:以上文献为模拟生成,实际研究中请根据具体蛋白背景(如CES4是否为泛素酶、羧酸酯酶等)检索真实文献。
The CES4 (N-term) antibody is specifically designed to target the N-terminal region of human carboxylesterase 4 (CES4), a member of the carboxylesterase enzyme family. Carboxylesterases (CES) are serine hydrolases involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics, including ester- and amide-containing drugs, environmental toxins, and endogenous lipids. CES4. encoded by the CES4A gene, is primarily expressed in the liver and gastrointestinal tract, where it plays a role in detoxification and drug activation. Its substrate specificity includes hydrolyzing compounds like irinotecan and clopidogrel, impacting pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy.
The CES4 (N-term) antibody is a valuable tool for detecting and quantifying CES4 protein expression in research applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. By targeting the N-terminal epitope, this antibody ensures specificity, minimizing cross-reactivity with other CES isoforms (e.g., CES1. CES2). Researchers utilize it to study CES4's tissue distribution, regulatory mechanisms, and involvement in drug metabolism or disease contexts, such as liver dysfunction or chemotherapy resistance. Its development underscores the growing interest in personalized medicine, where understanding interindividual variability in CES enzyme activity could optimize drug dosing and reduce adverse effects. Validation data, including knockout controls, are critical to confirming its reliability in experimental models.
×