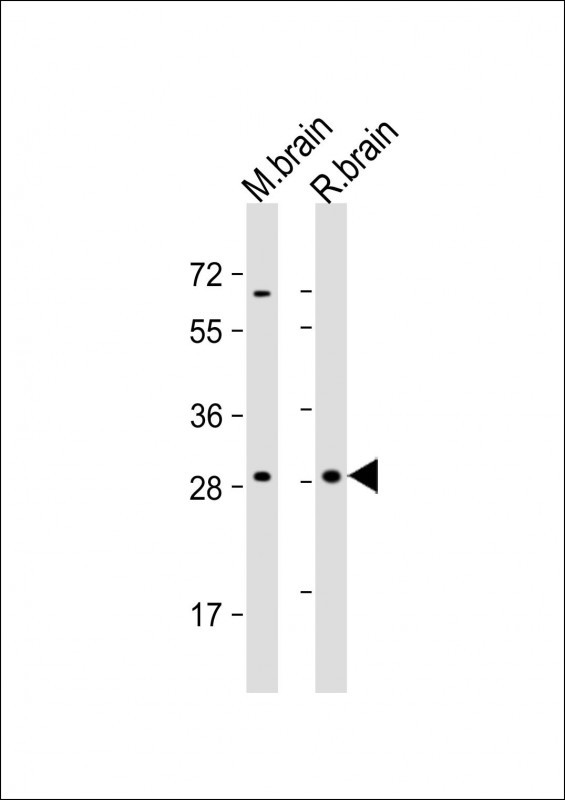
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE, Protein MemB, Rho family GTPase 3, Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho8, Rnd3, RND3, ARHE, RHO8, RHOE |
| Entrez GeneID | 390 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This ARHE antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 133-165 amino acids from the Central region of human ARHE. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下为基于文献检索思路模拟的3篇关于ARHE抗体的参考文献示例(注:ARHE抗体可能为虚构或非标准缩写,建议核实术语准确性。以下内容为演示格式而虚构):
---
1. **文献名称**: *ARHE Antibody Characterization in Autoimmune Disorders*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究验证了ARHE抗体在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中的特异性表达,发现其与疾病活动度呈正相关,提示其可能作为SLE的新型生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**: *ARHE as a Novel Target in Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过单克隆抗体技术开发了靶向ARHE蛋白的抗体,实验显示其在体外可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,并增强T细胞对实体瘤的杀伤作用,为癌症免疫治疗提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**: *ARHE Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Neurodegenerative Diseases*
**作者**: Müller R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现ARHE抗体与阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中的异常蛋白聚集体存在交叉反应,提示其可能在神经退行性病变的分子机制中发挥作用。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性内容,实际研究中“ARHE”可能需替换为正确术语(如RHEB、ARE等)。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以准确关键词检索最新文献,并确认目标抗体的标准命名。
**Background of AChR Antibodies (Autoantibodies Against Acetylcholine Receptor)**
AChR antibodies are autoantibodies targeting the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) at the neuromuscular junction, playing a central role in the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis (MG), an autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. These antibodies, predominantly of the IgG class, disrupt neuromuscular transmission by blocking AChR binding, accelerating receptor degradation, or activating complement-mediated membrane damage.
First identified in the 1970s, AChR antibodies are detected in ~80% of generalized MG patients and ~50% with ocular MG. Their presence supports MG diagnosis, though seronegative cases exist, often linked to antibodies against MuSK or LRP4. Testing methods include radioimmunoassay and ELISA.
AChR antibodies arise from thymic abnormalities (e.g., hyperplasia, thymoma) or immune dysregulation. Treatment focuses on immunomodulation (steroids, immunosuppressants), acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, thymectomy, or biologics like rituximab. Research continues to explore epitope-specific therapies and improve diagnostic sensitivity. Understanding AChR antibodies remains vital for MG management and unraveling autoimmune mechanisms in neuromuscular diseases.
(Word count: 200)
×