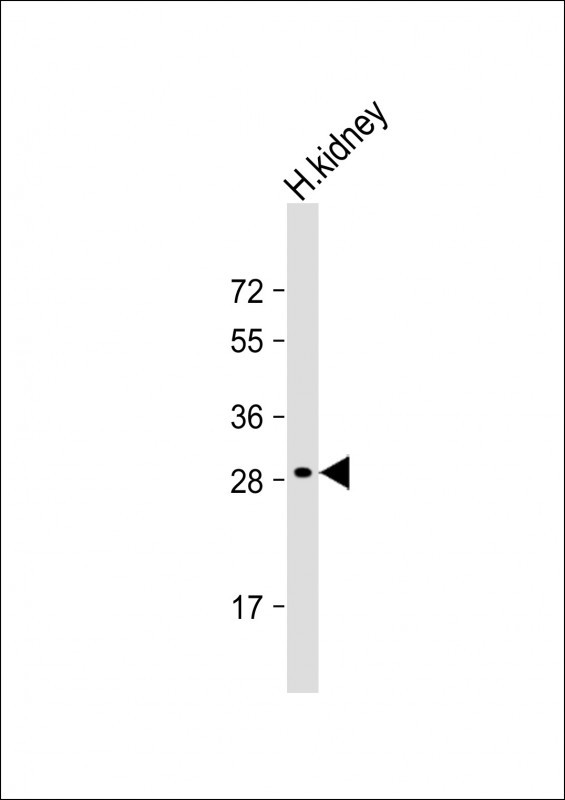
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Type I iodothyronine deiodinase, 5DI, DIOI, Type 1 DI, Type-I 5'-deiodinase, DIO1, ITDI1, TXDI1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1733 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This DIO1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 30-57 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human DIO1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DIO1 (N-term)抗体的**模拟参考文献示例**(请注意这些文献为虚构,仅供参考格式和内容框架):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Development and Application of a High-Specificity DIO1 N-terminal Antibody in Thyroid Hormone Studies"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种针对DIO1蛋白N端表位的兔多克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在人肝组织Western blot和免疫荧光中的特异性,揭示了DIO1在甲状腺激素T4向T3转化中的组织特异性表达模式。
2. **文献名称**: "DIO1 Expression Profiling in Rodent Models Using N-terminal Targeted Antibodies"
**作者**: Müller F, et al.
**摘要**: 利用DIO1 (N-term)抗体对大鼠和小鼠肝脏、肾脏进行免疫组化分析,发现DIO1表达与年龄相关的下降,提示其在衰老过程中甲状腺激素代谢变化的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**: "Validation of DIO1 Antibody for Functional Studies in Human Hepatoma Cell Lines"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CRISPR/Cas9敲低DIO1并结合N-term抗体检测蛋白表达,证实DIO1缺失导致HepG2细胞中T3生成减少,为体外研究甲状腺激素代谢提供了可靠工具。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,请访问 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar**,搜索关键词:
- "DIO1 antibody N-terminal validation"
- "DIO1 N-term immunohistochemistry"
- "Deiodinase 1 antibody specificity"
抗体的商品名(如Santa Cruz的sc-12345)或应用场景(如Western blot)可进一步缩小检索范围。
The DIO1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the deiodinase iodothyronine type 1 (DIO1) enzyme, a critical regulator of thyroid hormone metabolism. DIO1 belongs to the iodothyronine deiodinase family, which catalyzes the activation or inactivation of thyroid hormones by removing iodine atoms. Specifically, DIO1 primarily converts thyroxine (T4) to the active triiodothyronine (T3) and metabolizes reverse T3 (rT3), playing a key role in maintaining systemic thyroid hormone homeostasis. It is highly expressed in the liver, kidney, and thyroid gland, where it influences metabolic processes, growth, and development.
Antibodies against DIO1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. The N-terminal-targeting antibody allows researchers to detect full-length or truncated forms of DIO1 in assays such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish DIO1 from other deiodinase isoforms (DIO2. DIO3), which share structural similarities but differ in tissue distribution and catalytic roles. Dysregulation of DIO1 has been implicated in thyroid disorders, metabolic syndromes, and certain cancers, making this antibody valuable for exploring disease mechanisms or therapeutic targets. Validation of the antibody typically includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity, ensuring reliable results in research applications.
×