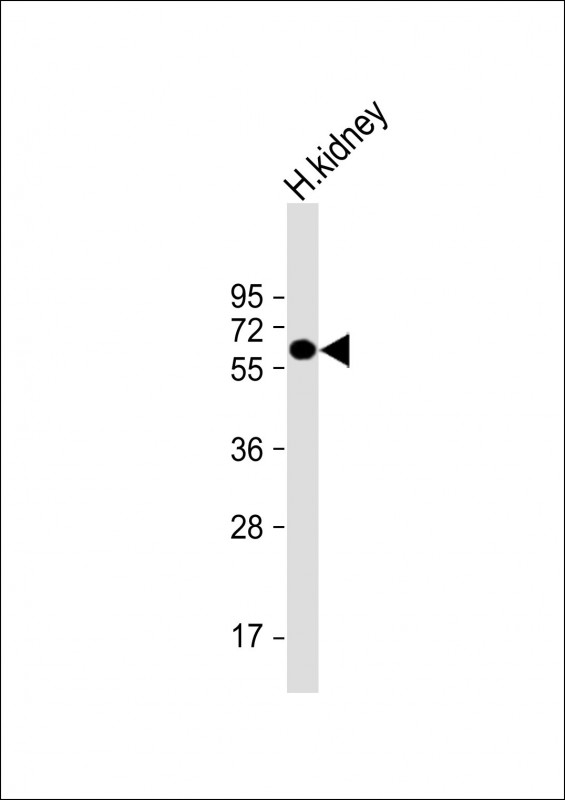
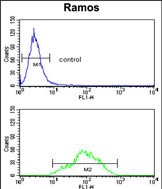
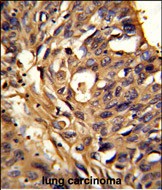
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, mitochondrial, ETF-QO, ETF-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, Electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase, ETF dehydrogenase, ETFDH |
| Entrez GeneID | 2110 |
| WB Predicted band size | 68.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ETFDH antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 32-61 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ETFDH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ETFDH(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in ETFDH cause riboflavin-responsive multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency*
**作者**:Olsen RKJ et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过分析患者成纤维细胞,发现ETFDH基因突变导致脂肪酸氧化缺陷。研究中使用了针对ETFDH蛋白N端的抗体进行Western blot分析,证实突变导致蛋白表达量显著降低,为疾病机制和诊断提供了依据。
2. **文献名称**:*Electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase: Structure, function and role in disease*
**作者**:Henriques BJ et al.
**摘要**:本文综述了ETFDH蛋白的结构与功能,并探讨其突变相关的代谢疾病。文献提到利用N端特异性抗体检测不同组织中的ETFDH表达水平,揭示了该蛋白在线粒体能量代谢中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel ETFDH mutation in a patient with late-onset glutaric aciduria type III*
**作者**:Yildiz Y et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一例迟发性戊二酸尿症III型患者的ETFDH新发突变。通过N端抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,显示突变导致ETFDH蛋白稳定性下降及线粒体定位异常,为临床表型与基因型关联提供了证据。
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或学术数据库核对最新研究。
The ETFDH (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Dehydrogenase (ETFDH), a critical enzyme in mitochondrial energy metabolism. ETFDH, located on the inner mitochondrial membrane, facilitates electron transfer from flavoproteins to the ubiquinone pool in the electron transport chain, playing a vital role in fatty acid β-oxidation and amino acid catabolism. Mutations in the ETFDH gene are associated with metabolic disorders such as glutaric acidemia type II (GA-II) or multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD), characterized by disrupted energy production and accumulation of toxic metabolites.
The ETFDH (N-term) antibody is commonly generated in immunized hosts (e.g., rabbits or mice) using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal epitope. Its specificity is validated through techniques like western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, often confirmed using ETFDH-knockout controls. Researchers utilize this antibody to study ETFDH expression patterns, subcellular localization, and potential post-translational modifications in tissues or cell lines. It also aids in diagnosing ETFDH-related disorders by detecting protein deficiencies or abnormalities in patient samples. By targeting the N-terminal region, this antibody helps elucidate structural or functional insights, particularly in disease mechanisms or therapeutic development for mitochondrial metabolic syndromes.
×