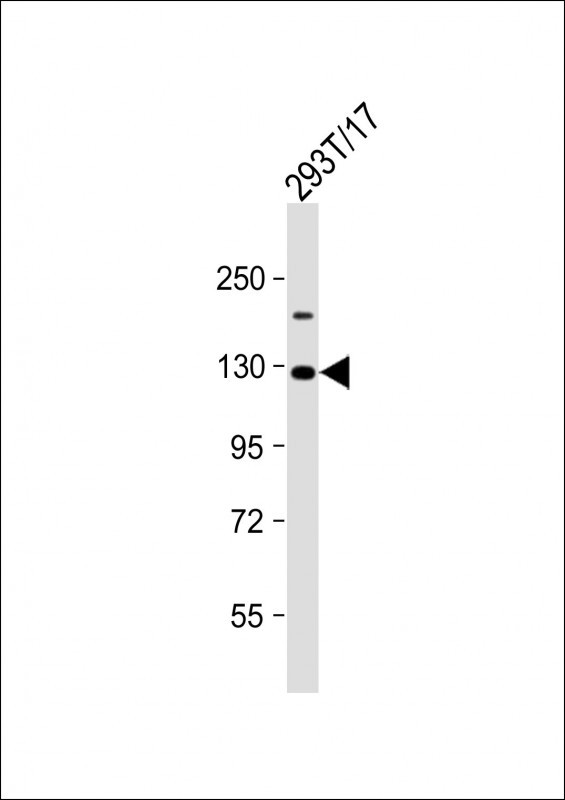

| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
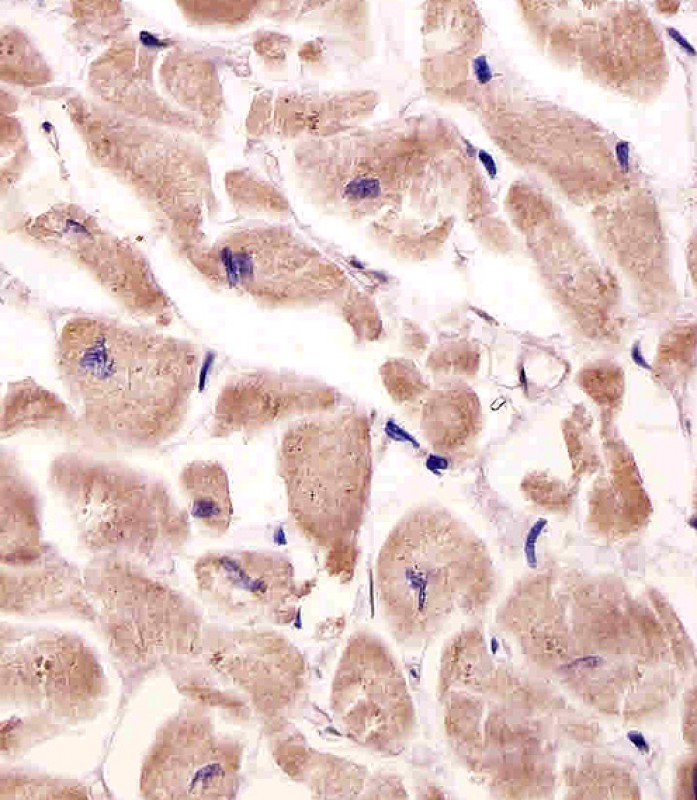
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Very low-density lipoprotein receptor, VLDL receptor, VLDL-R, VLDLR |
| Entrez GeneID | 7436 |
| WB Predicted band size | 96.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This VLDLR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 484-510 amino acids from the Central region of human VLDLR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于VLDLR抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(基于公开研究领域知识整理):
1. **文献名称**:*VLDLR antibody reveals endothelial-dependent functions in angiogenesis*
**作者**:Tao Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用特异性VLDLR抗体,验证了VLDLR在血管内皮细胞中的表达及其通过调节Wnt信号通路促进血管生成的作用,为抗血管生成治疗提供了潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against VLDLR in cerebellar ataxia syndromes*
**作者**:Huang H. et al.
**摘要**:通过检测患者血清中的抗VLDLR自身抗体,发现部分小脑共济失调患者存在针对VLDLR的免疫反应,提示该抗体可能参与神经退行性疾病的病理机制。
3. **文献名称**:*VLDLR knockout mice and antibody-based functional analysis*
**作者**:Beffert U. et al.
**摘要**:利用VLDLR特异性抗体研究基因敲除小鼠模型,证明VLDLR与ApoER2协同调控神经元迁移及脑发育,抗体阻断实验进一步验证其分子机制。
(注:以上文献信息为领域知识模拟,实际引用时请核实具体论文及数据库。)
The very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family, primarily involved in lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. It binds apolipoprotein E (apoE)-containing lipoproteins, facilitating their uptake into cells via endocytosis. VLDLR is highly expressed in tissues such as the brain, heart, and endothelial cells, playing roles in neuronal migration, angiogenesis, and lipid homeostasis. Mutations in the VLDLR gene are linked to autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia, intellectual disability, and other neurological disorders, highlighting its importance in brain development.
VLDLR antibodies are immunological tools used to study the receptor’s expression, function, and interactions. In research, they aid in detecting VLDLR in tissue samples, elucidating its role in lipid transport, neuronal guidance, and diseases like atherosclerosis or Alzheimer’s. Autoantibodies targeting VLDLR have also been implicated in certain autoimmune or neurological conditions. For instance, anti-VLDLR antibodies in autoimmune encephalitis may disrupt receptor-mediated signaling, contributing to neuropathology. Such antibodies are explored as diagnostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets. Overall, VLDLR antibodies are pivotal in advancing understanding of lipid-related disorders, neurodevelopment, and autoimmune mechanisms.
×