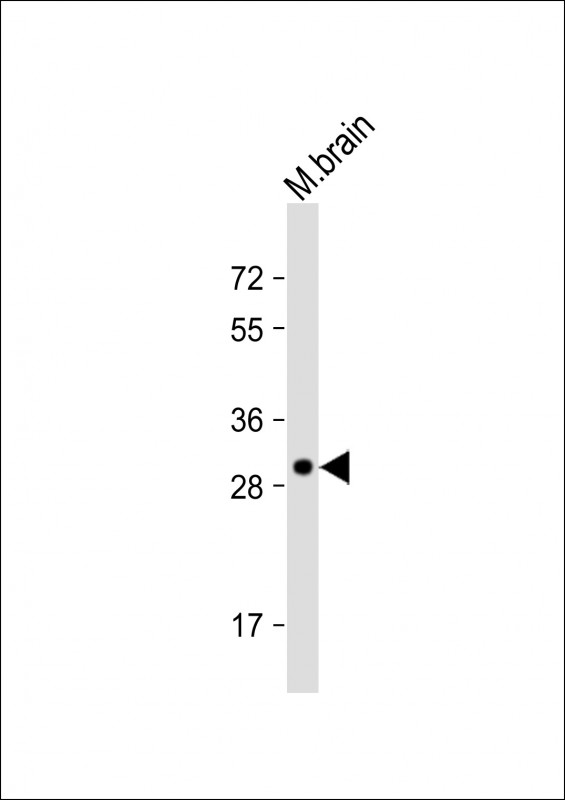
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Dysbindin, Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 subunit 8, BLOC-1 subunit 8, Dysbindin-1, Dystrobrevin-binding protein 1, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 7 protein homolog, HPS7 protein homolog, Dtnbp1, Bloc1s8, Sdy |
| Entrez GeneID | 94245 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This Dtnbp1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 296-325 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human Dtnbp1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DTNBP1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "Dysbindin-1 in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia cases"
**作者**: Weickert CS et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用DTNBP1抗体检测精神分裂症患者背外侧前额叶皮层中dysbindin蛋白水平,发现患者该蛋白表达显著降低,提示其与突触功能异常相关。
2. **文献名称**: "Dysbindin-1 reductions in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia are genotype-dependent"
**作者**: Talbot K et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化结合DTNBP1抗体,发现精神分裂症患者前额叶皮层中dysbindin蛋白表达下降,且与特定单核苷酸多态性(SNP)相关,表明遗传变异影响蛋白表达。
3. **文献名称**: "DTNBP1 gene knockdown impairs neurite outgrowth and synaptic formation"
**作者**: Kumamoto N et al.
**摘要**: 研究在小鼠神经元中使用DTNBP1抗体追踪蛋白定位,发现基因敲减导致树突发育和突触形成受损,证明dysbindin对神经发育的关键作用。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需核对原文准确性。)
The DTNBP1 (Dystrobrevin Binding Protein 1) gene encodes dysbindin, a protein implicated in synaptic function and neurodevelopmental processes. Dysbindin is a component of the BLOC-1 (Biogenesis of Lysosome-Related Organelles Complex 1), involved in intracellular trafficking, particularly in lysosome-related organelles and neurotransmitter release. It is highly expressed in the brain, including regions like the hippocampus, cortex, and striatum. DTNBP1 gained attention due to its association with schizophrenia risk; genetic studies link certain DTNBP1 variants to altered protein expression and cognitive deficits in psychiatric disorders. Dysbindin deficiency in animal models correlates with reduced synaptic plasticity, altered dopamine/glutamate signaling, and behavioral abnormalities resembling schizophrenia phenotypes.
Antibodies targeting DTNBP1/dysbindin are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein levels in brain tissues, cell lines, or disease models. These antibodies help investigate dysbindin’s role in neurodevelopmental disorders, synaptic vesicle dynamics, and interactions with partners like dystrobrevin or snapin. Some studies also utilize DTNBP1 antibodies to explore dysregulation in postmortem brains of schizophrenia patients or in cellular models of lysosomal trafficking defects. However, antibody specificity remains a consideration, as dysbindin isoforms and tissue-specific post-translational modifications may affect detection. Validated antibodies are critical for clarifying DTNBP1’s pathophysiological contributions and therapeutic potential.
×