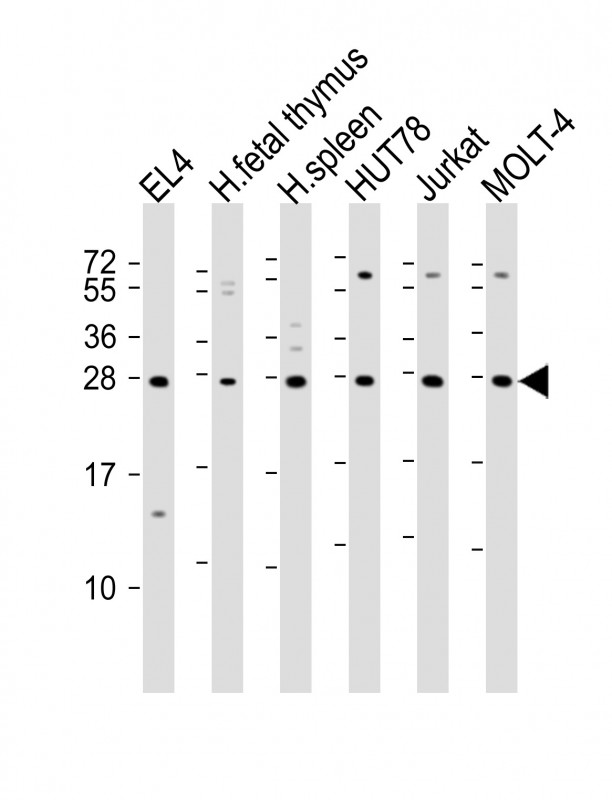
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 9, V-set and transmembrane domain-containing protein 3, TIGIT, VSIG9, VSTM3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 201633 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This TIGIT antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 12-142 amino acids from human TIGIT. |
+ +
以下是关于TIGIT抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖机制研究、临床试验及综述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*TIGIT and PD-1 dual checkpoint blockade enhances antitumor immunity and survival*
**作者**:Chauvin, J.M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究(2018年发表于*Cell*)揭示了TIGIT与PD-1在肿瘤微环境中的协同抑制作用。通过临床前模型证明,联合阻断TIGIT和PD-1可显著增强CD8+ T细胞功能,抑制肿瘤生长并延长生存期,为后续临床试验提供了理论基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab in NSCLC: A phase II trial*
**作者**:Rodriguez-Abreu, D., et al.
**摘要**:这项Ⅱ期临床试验(2020年发表于*Lancet Oncology*)评估了TIGIT抗体tiragolumab联合PD-L1抑制剂atezolizumab治疗非小细胞肺癌的效果。结果显示联合疗法显著提高客观缓解率(ORR)和无进展生存期(PFS),成为首个验证TIGIT/PD-L1双靶点临床潜力的研究。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting TIGIT in cancer immunotherapy: From mechanistic insights to clinical development*
**作者**:Banta, K.L., et al.
**摘要**:2021年发表于*Nature Reviews Drug Discovery*的综述,系统总结了TIGIT在调节T细胞和NK细胞功能中的作用机制,梳理了当前TIGIT抗体的临床开发进展,并讨论了其与现有免疫疗法的联合应用策略及挑战。
---
如需更多文献或特定研究方向(如实体瘤/血液瘤),可进一步补充说明。
**Background of TIGIT Antibodies**
TIGIT (T-cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin and ITIM domains) is an inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor expressed on T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs). It belongs to the CD28 family and interacts with ligands such as CD155 (PVR), which is often overexpressed on tumor cells and antigen-presenting cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). By binding to CD155. TIGIT suppresses anti-tumor immunity through multiple mechanisms: dampening T/NK cell activation, promoting Treg immunosuppressive functions, and competing with the co-stimulatory receptor CD226 for ligand binding.
The therapeutic potential of TIGIT blockade emerged as a strategy to overcome resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, which revolutionized cancer treatment but show limited efficacy in many patients. Preclinical studies demonstrated that anti-TIGIT antibodies restore T/NK cell effector functions and synergize with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors to enhance anti-tumor responses. Early-phase clinical trials (e.g., tiragolumab, vibostolimab) showed promising results, particularly in PD-L1-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), leading to phase III evaluations. However, recent trials reported mixed outcomes, highlighting the need to refine patient selection, dosing, and combination strategies.
Current research focuses on understanding TIGIT's complex biology, identifying predictive biomarkers, and optimizing combination therapies to unlock its full potential in cancer immunotherapy.
×