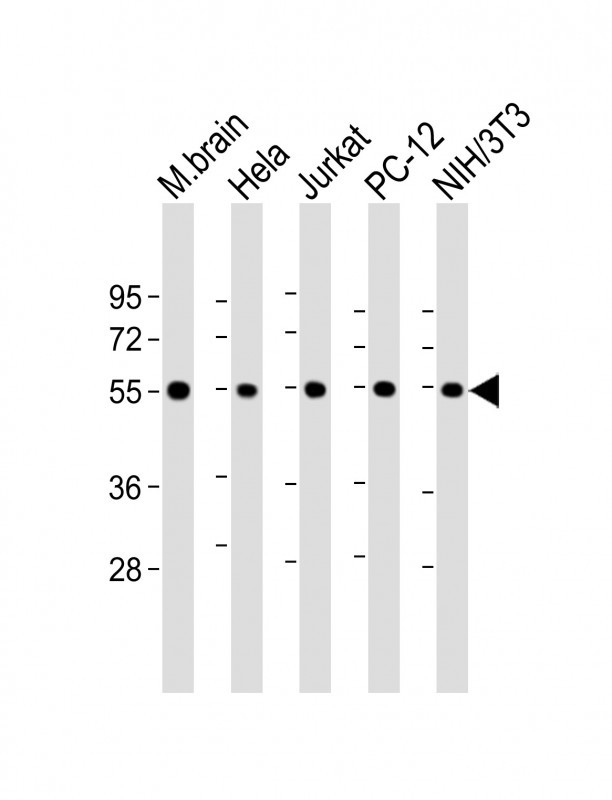
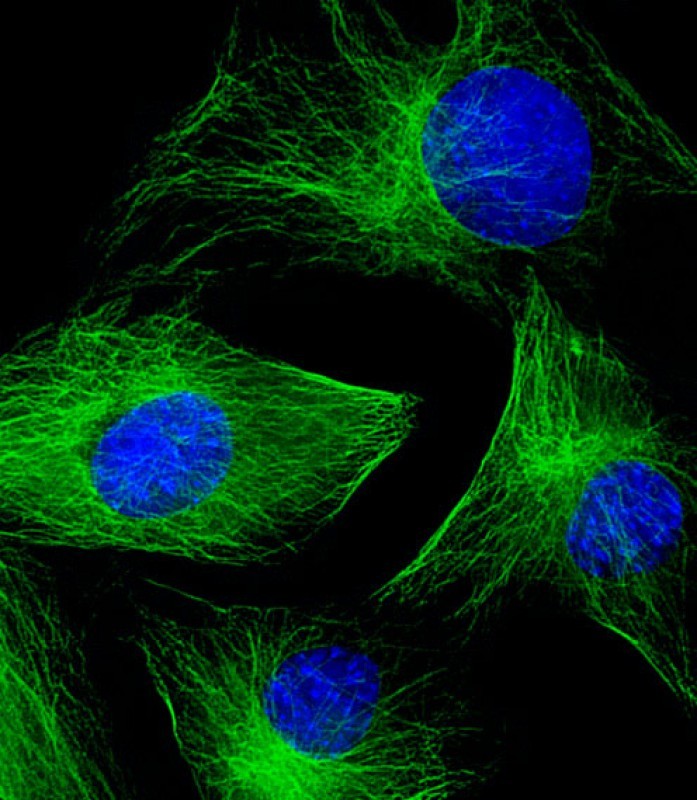
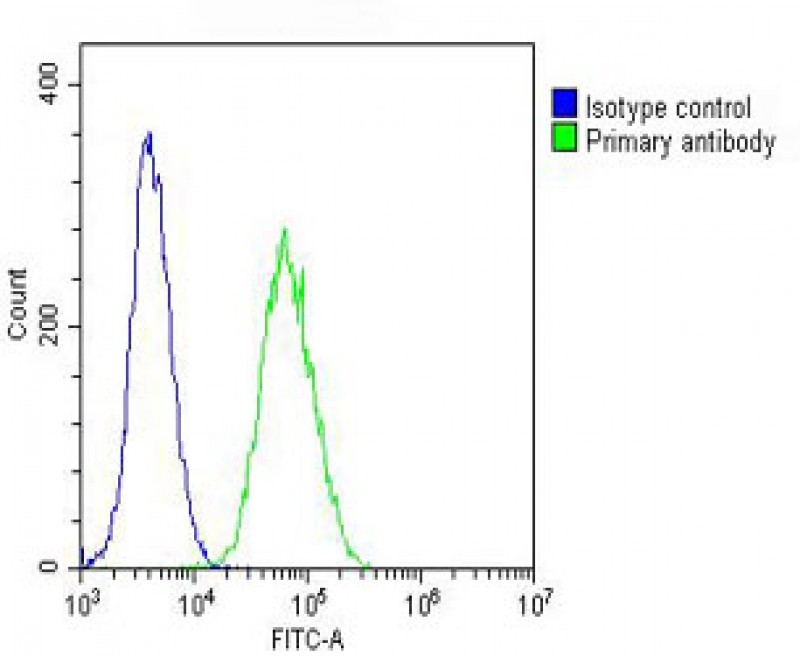
| WB | 1/8000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tubulin beta-2A chain, Tubb2a, Tubb2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 22151 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 14-46 amino acids from human. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于beta II Tubulin(TUBB2B)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"TUBB2B mutation causes isolated ocular motility defect and ciliopathy spectrum"*
**作者**: Patel et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用beta II Tubulin特异性抗体,揭示了TUBB2B基因突变与先天性眼球运动障碍及纤毛病表型的关联,证实该抗体在神经元纤毛结构分析中的有效性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Antibody-based profiling of βII-tubulin isoforms in human cancers"*
**作者**: Smith et al.
**摘要**: 通过开发高特异性beta II Tubulin单克隆抗体,作者系统分析了多种癌症组织中βII-tubulin的异常表达模式,提示其作为肿瘤分型生物标志物的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Selective neuronal vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease via βII-tubulin degradation"*
**作者**: Lee et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用beta II Tubulin抗体标记海马神经元,发现阿尔茨海默病模型中该蛋白的异常降解机制,为神经元退行性病变提供了新机制解释。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。若需具体文章,建议补充时间范围或研究领域以进一步筛选。
Beta II Tubulin (βIII-Tubulin), a member of the tubulin protein family, is a cytoskeletal component essential for microtubule formation. Microtubules play critical roles in cell structure, intracellular transport, and mitosis. Unlike the ubiquitously expressed beta I Tubulin, beta II Tubulin (encoded by the TUBB3 gene) is neuron-specific and serves as a marker for differentiating neurons during development. Its expression is particularly prominent in postmitotic neurons, where it contributes to axonal growth, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter release.
Antibodies targeting beta II Tubulin are widely used in neuroscience and cancer research. In neurobiology, they help identify neuronal populations, track neurogenesis, and study neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. In oncology, beta II Tubulin overexpression correlates with aggressive tumors and resistance to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutics (e.g., taxanes), making it a prognostic biomarker. These antibodies are also employed to assess mitotic activity in dividing cells.
Commercially available beta II Tubulin antibodies are typically validated for techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Specificity is crucial, as cross-reactivity with other beta-tubulin isoforms (e.g., beta I or beta IV) can occur depending on epitope recognition. Some studies use beta II Tubulin antibodies as loading controls in neuronal tissues due to its stable expression. Ongoing research explores its role in cellular stress responses and interactions with microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs), further expanding its biomedical relevance.
×