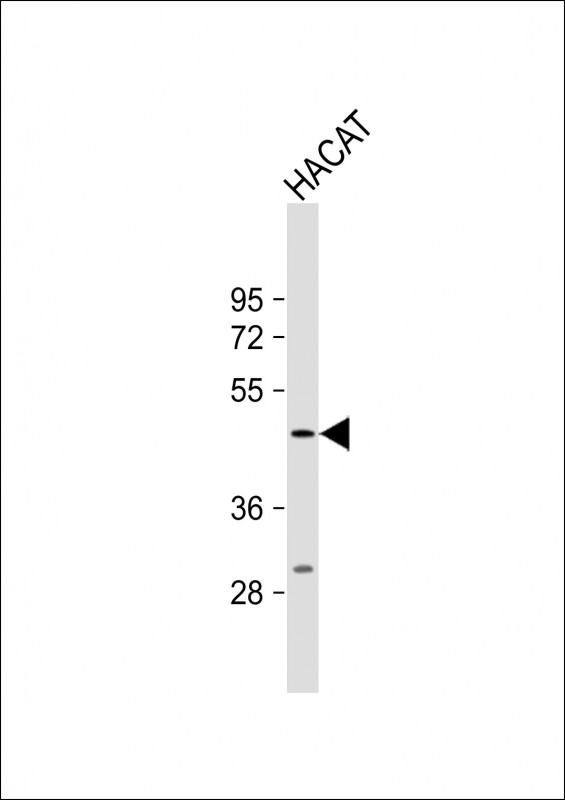
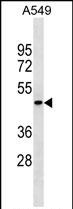
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Peptidoglycan recognition protein 4, Peptidoglycan recognition protein I-beta, PGLYRPIbeta, PGRP-I-beta, Peptidoglycan recognition protein intermediate beta, PGLYRP4, PGRPIB |
| Entrez GeneID | 57115 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PGLYRP4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 242-268 amino acids from the Central region of human PGLYRP4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PGLYRP4抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein 4 Limits Bacterial Clearance and Inflammation in the Intestine*
**作者**:Dziarski R, et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨PGLYRP4在小鼠肠道免疫中的作用,通过特异性抗体检测其表达水平,发现其通过调控炎症因子抑制过度免疫反应,从而维持肠道菌群平衡。
2. **文献名称**:*Antibacterial Activity of Human PGLYRP4 Requires Proteolytic Processing*
**作者**:Saha S, et al.
**摘要**:利用抗PGLYRP4抗体研究其蛋白活性,发现其在体外经酶切后释放抗菌肽,直接杀伤革兰氏阳性菌,揭示了其作为先天免疫效应分子的机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Differential Expression of PGLYRP4 in Psoriatic Skin and Its Role in Keratinocyte Inflammation*
**作者**:Tydell CC, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析银屑病患者皮肤样本,发现PGLYRP4在病变区域高表达,抗体阻断实验表明其通过TLR通路加剧角质细胞炎症反应,提示其参与皮肤病理性过程。
4. **文献名称**:*PGLYRP4 Modulates Autophagy in Macrophages to Control Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection*
**作者**:Liu Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用PGLYRP4抗体探究巨噬细胞自噬调控机制,发现其通过结合细胞内膜系统促进自噬体形成,增强宿主对结核分枝杆菌的清除能力。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对真实数据库及原文内容。)
Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein 4 (PGLYRP4) is a member of the peptidoglycan recognition protein family, which plays a role in innate immunity by detecting pathogen-associated molecular patterns, particularly bacterial peptidoglycan. PGLYRP4 is expressed in various tissues, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and immune cells, and functions as a pattern recognition receptor to activate antimicrobial and inflammatory responses. Antibodies targeting PGLYRP4 are valuable tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles in host defense and disease contexts.
PGLYRP4 antibodies are commonly developed in animal models (e.g., mice, rabbits) using recombinant proteins or peptide antigens. These antibodies enable researchers to investigate PGLYRP4’s involvement in inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, and infections by detecting protein levels via techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry. Studies suggest PGLYRP4 may modulate immune tolerance and inflammation, with potential links to conditions like psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, or rheumatoid arthritis. Neutralizing antibodies against PGLYRP4 are also explored for therapeutic applications, aiming to regulate dysregulated immune responses. However, the exact mechanisms and clinical relevance of PGLYRP4 in human diseases remain under investigation, necessitating further research using these antibodies to clarify its pathophysiological roles.
×