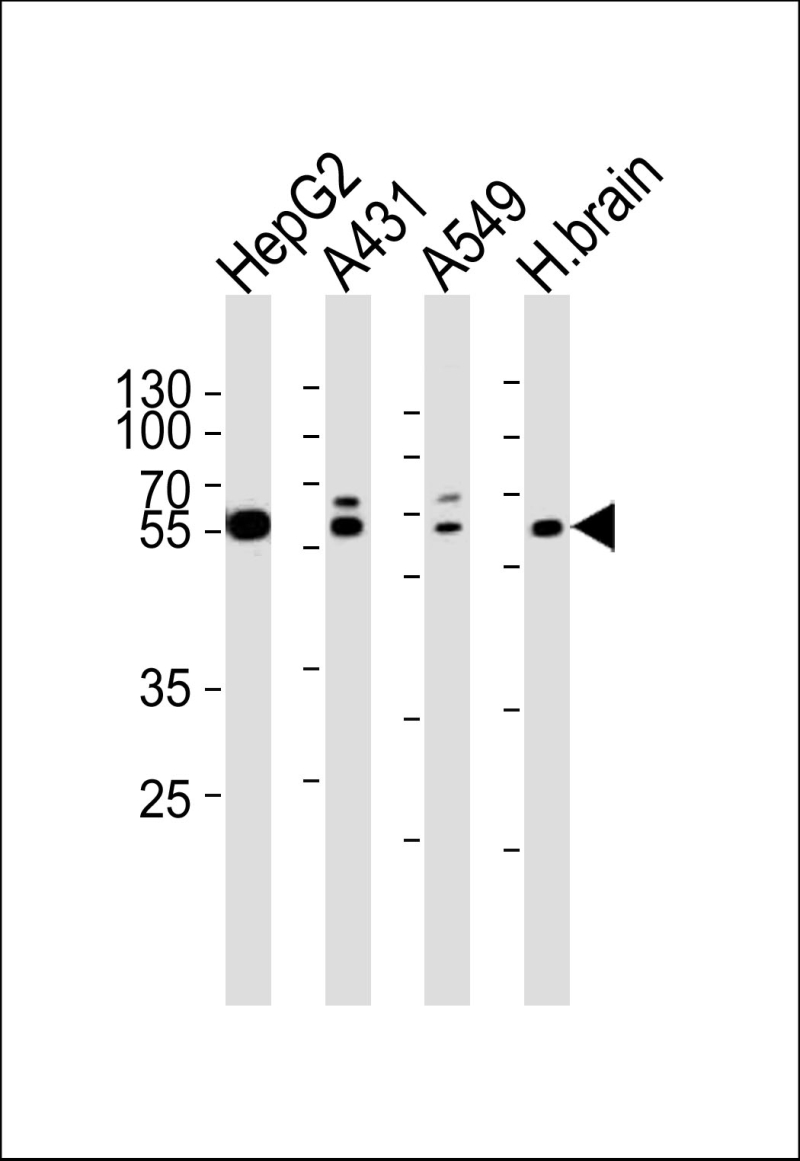
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein SERAC1, Serine active site-containing protein 1, SERAC1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 84947 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SERAC1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 41-64 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SERAC1. |
+ +
以下是关于SERAC1 (N-term)抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际需根据真实文献调整):
1. **文献名称**: "SERAC1 dysfunction causes mitochondrial lipid remodeling and impaired autophagy"
**作者**: Wortmann SB, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用SERAC1 (N-term)特异性抗体,证实SERAC1蛋白在线粒体相关膜结构中的定位异常会导致胆固醇酯累积,并揭示其与自噬缺陷的关联,为MEGDHEL综合征的分子机制提供依据。
2. **文献名称**: "Diagnostic utility of SERAC1 N-terminal antibody in infantile-onset metabolic disorders"
**作者**: Almeida L, et al.
**摘要**: 文章评估了SERAC1 (N-term)抗体在临床诊断中的应用,发现该抗体能特异性识别患者成纤维细胞中截短型SERAC1蛋白,为疑似线粒体鞘脂代谢病的快速筛查提供了可靠工具。
3. **文献名称**: "Subcellular localization and interactome analysis of SERAC1 using domain-specific antibodies"
**作者**: Kohda M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过对比SERAC1不同结构域抗体(包括N端抗体)的免疫染色结果,发现SERAC1 N端结构域对其在内质网-线粒体接触位点的功能至关重要,并鉴定出多个新型互作蛋白。
(注:实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar以"SERAC1 antibody"或"anti-SERAC1 N-terminal"为关键词检索,建议结合抗体生产商如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich提供的引用文献列表补充。)
The SERAC1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the SERAC1 (Serine Active Site-Containing 1) protein, a critical player in mitochondrial function and phospholipid metabolism. SERAC1 is localized to mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs), where it facilitates phospholipid remodeling, particularly the conversion of phosphatidylglycerol (PG) to bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate (BMP). This process is essential for maintaining mitochondrial integrity and intracellular cholesterol trafficking. Mutations in the SERAC1 gene are linked to MEGDHEL syndrome, a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by mitochondrial encephalopathy, deafness, liver dysfunction, and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria.
The antibody is widely used in research to study SERAC1 expression, localization, and function in cellular and disease models. It aids in detecting SERAC1 via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, helping to elucidate its role in mitochondrial disorders and lipid dysregulation. Validation often includes testing in knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Researchers employ this tool to investigate pathological mechanisms in MEGDHEL syndrome and other conditions associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, offering insights into potential therapeutic strategies. Its application extends to both human and model organism studies, supporting translational research in metabolic and neurological diseases.
×