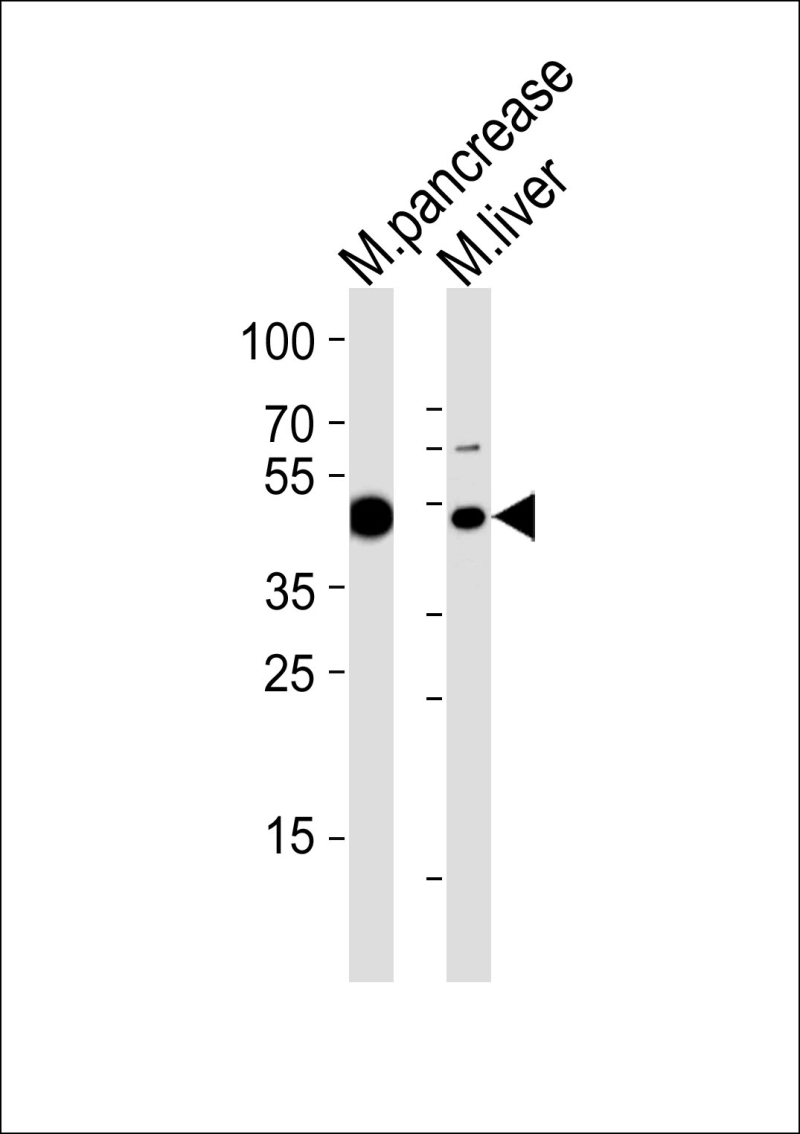
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Brachyury protein, Protein T, T |
| Entrez GeneID | 20997 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | This Mouse T antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 408-442 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human Mouse T. |
+ +
以下是3篇与Mouse T抗体相关的研究文献摘要示例:
1. **"Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against mouse CD3"**
- 作者:Kisielow, P. et al.
- 摘要:报道了针对小鼠CD3ε链的单克隆抗体的开发,用于T细胞受体(TCR)复合物的特异性检测,为流式细胞术和T细胞功能研究提供工具。
2. **"Structural basis of T cell receptor recognition by anti-CD3 antibodies"**
- 作者:Kjer-Nielsen, L. et al.
- 摘要:通过X射线晶体学解析了小鼠TCR与抗CD3抗体的结合模式,揭示了抗体调控T细胞活化的分子机制,为免疫疗法设计提供结构基础。
3. **"Targeting T cell malignancies using anti-CD4 CAR-T cells"**
- 作者:Mamonkin, M. et al.
- 摘要:研究利用抗小鼠CD4抗体制备CAR-T细胞,在小鼠模型中有效清除CD4+ T细胞淋巴瘤,验证了抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的应用潜力。
4. **"Novel anti-mouse CTLA-4 antibodies enhance antitumor immunity"**
- 作者:Selby, M.J. et al.
- 摘要:开发了阻断小鼠CTLA-4的抗体,证明其能增强T细胞抗肿瘤反应,为检查点抑制剂在小鼠模型中的临床前研究提供工具。
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认。
Mouse T antibodies, primarily referring to antibodies targeting T cell-specific markers or receptors in mice, are essential tools in immunology research. These antibodies are typically generated against surface proteins like CD3. CD4. CD8. or components of the T cell receptor (TCR) complex, enabling the identification and isolation of specific T cell subsets. Developed through hybridoma technology or recombinant methods, mouse-derived T antibodies exhibit high specificity and reproducibility, making them critical for flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional studies in murine models.
Their significance lies in dissecting T cell biology, including activation, differentiation, and effector functions. For example, anti-CD3 antibodies can stimulate TCR signaling, mimicking antigen recognition, while anti-CD4/CD8 antibodies help classify helper and cytotoxic T cells. Additionally, they facilitate research on immune disorders, such as autoimmune diseases and cancer immunotherapy. Mouse models treated with checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-CTLA-4 or anti-PD-1 antibodies) rely on these reagents to evaluate therapeutic efficacy and immune responses.
However, cross-reactivity with non-target species and potential batch variability require careful validation. Advances in monoclonal antibody engineering, including isotype controls and fluorochrome conjugation, have enhanced their precision. As murine systems remain foundational for translational studies, Mouse T antibodies continue to bridge experimental insights and clinical applications in adaptive immunity research.
×