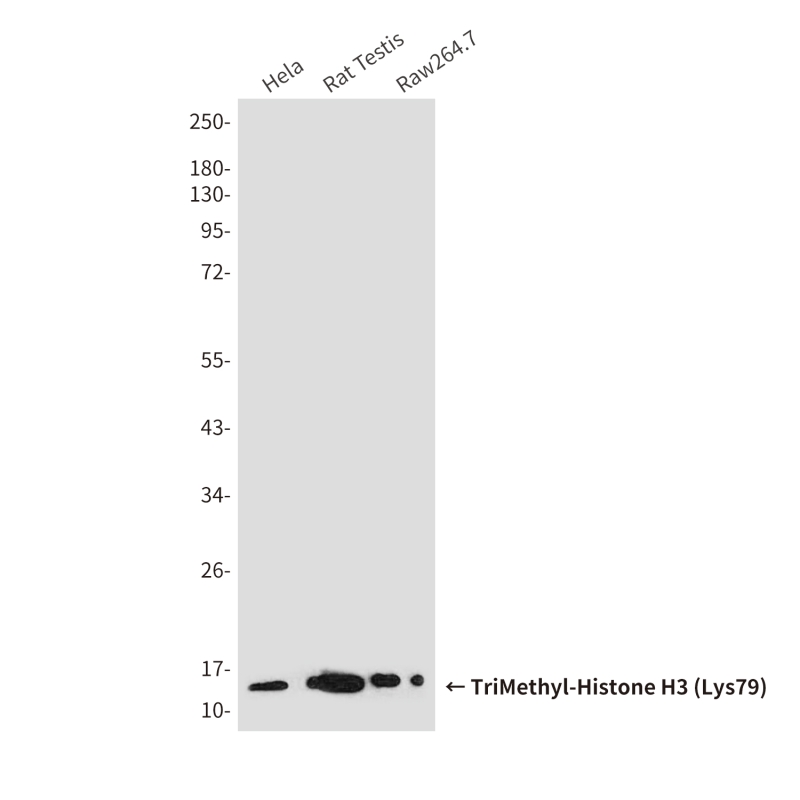
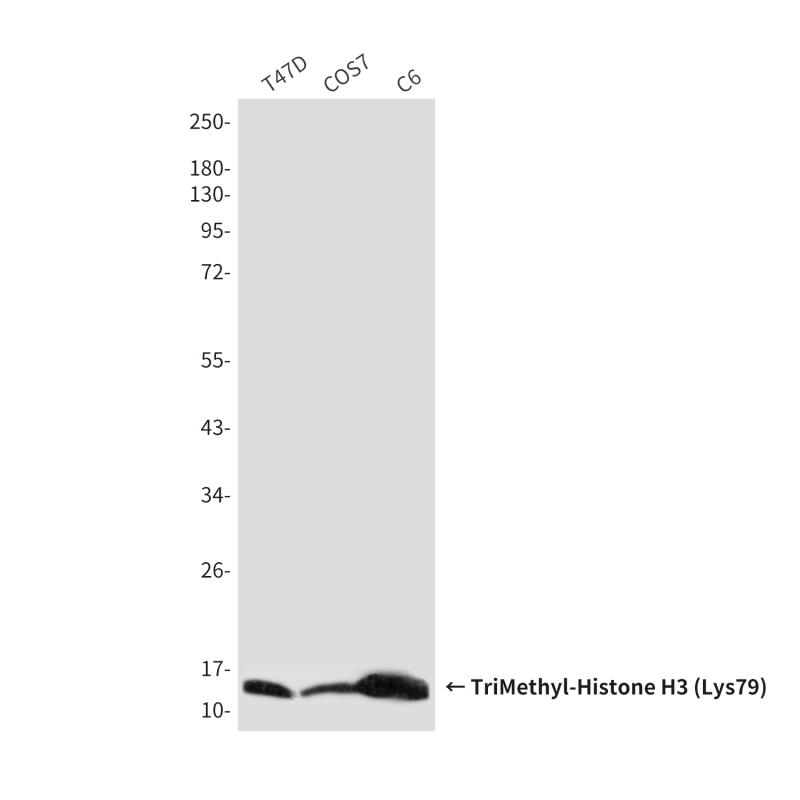
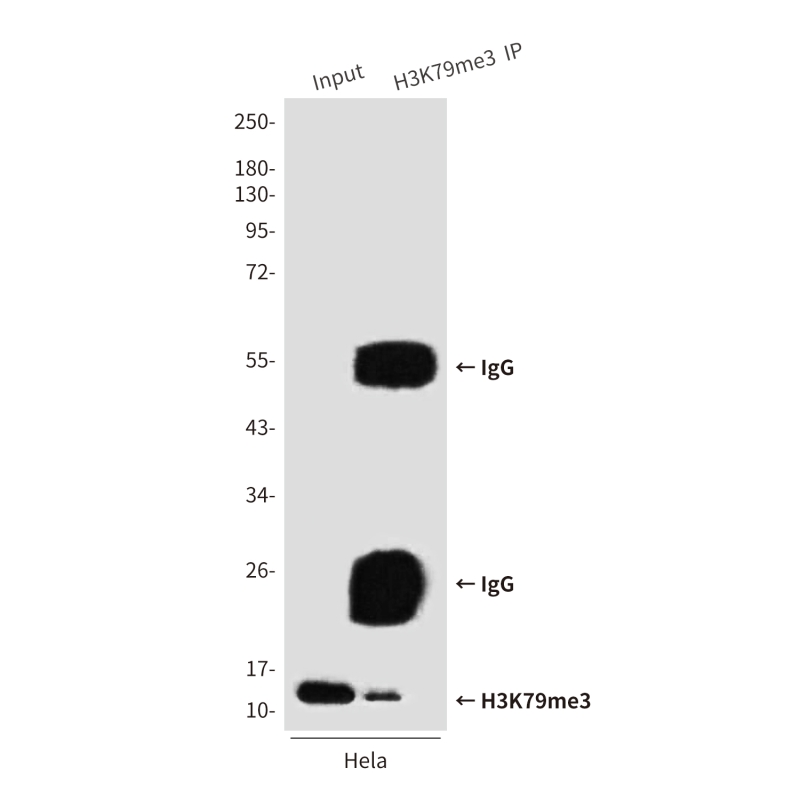
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H3K79me3; H3 histone; HIST1H3A; Histone cluster 1; H3a |
| Entrez GeneID | 8350 |
| clone | 5C6 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 15 kDa; Observed MW: 15 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of Histone H3 (Tri Methyl Lys79) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于H3K79三甲基化(H3K79me3)及其相关抗体的参考文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*DOT1L/KMT4 Recruitment and H3K79 Methylation Are Ubiquitously Coupled with Gene Transcription in Mammalian Cells*
**作者**:Steger, D.J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过ChIP-seq和抗体特异性分析,揭示DOT1L介导的H3K79me3广泛分布于哺乳动物基因的转录活跃区域,并证明其与RNA聚合酶II的转录延伸密切相关,为H3K79me3在基因表达调控中的全局作用提供证据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*H3K79 Methylation Profiles Define Murine and Human MLL-AF4 Leukemias*
**作者**:Okada, Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用H3K79me3特异性抗体发现,MLL-AF4融合蛋白通过异常招募DOT1L,导致白血病相关基因启动子区H3K79me3水平升高,驱动白血病发生,提示H3K79me3可作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The Role of H3K79 Methylation in the DNA Damage Response*
**作者**:Huyen, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该文发现H3K79me3在DNA损伤修复中起关键作用,通过特异性抗体检测证明其修饰水平变化影响53BP1等修复蛋白的招募,阐明其在维持基因组稳定性中的机制。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Selective Inhibition of DOT1L Methyltransferase by Cyclic Disulfide Disrupts H3K79me2/3 and Targets Leukemia Stem Cells*
**作者**:Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种小分子抑制剂靶向DOT1L,利用H3K79me3抗体验证其降低甲基化水平的效果,并证明该策略可选择性清除白血病干细胞,为表观遗传疗法提供新思路。
---
这些文献均涉及H3K79me3的生物学功能研究,并通过特异性抗体进行检测或机制验证。
The TriMethyl-Histone H3 (Lys79) antibody is a key tool for studying post-translational modifications of histone H3. specifically recognizing trimethylation at lysine 79 (H3K79me3). This epigenetic mark is associated with transcriptionally active chromatin and plays roles in gene regulation, DNA repair, and cell cycle control. H3K79 methylation occurs within the globular core of the histone, a unique location compared to other modifications in the N-terminal tail. The modification is catalyzed by the methyltransferase DOT1L, which is the only known enzyme responsible for this mark in mammals.
H3K79me3 is enriched in gene bodies of actively transcribed genes, suggesting its involvement in transcriptional elongation. It also participates in DNA damage response pathways and maintains genomic stability. Dysregulation of H3K79 methylation has been linked to cancers, particularly leukemias with MLL gene rearrangements, where aberrant DOT1L activity drives oncogenic gene expression.
Researchers use this antibody in techniques like chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunofluorescence, and Western blot to map H3K79me3 distribution, investigate its functional roles, and explore its therapeutic implications. Its specificity is critical for distinguishing trimethylation from mono- or dimethylated states, which may have distinct biological outcomes. Proper validation, including knockout cell controls, is essential due to potential cross-reactivity with other histone modifications.
×