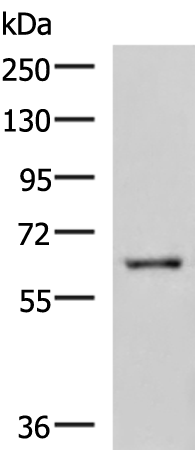
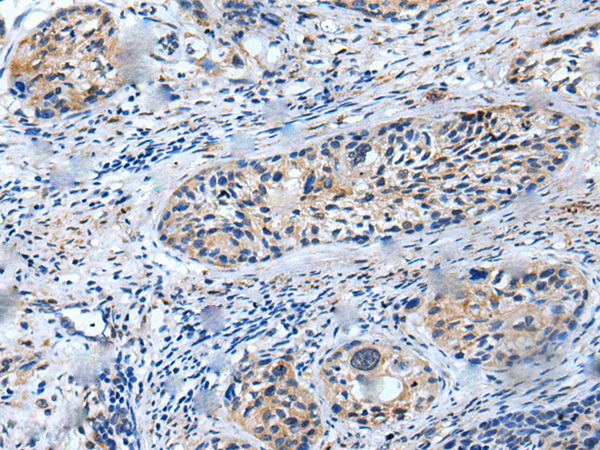
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LIR8; CD85C; LIR-8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 64 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human LILRB5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LILRB5抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*LILRB5 antibody blockade enhances T cell activity in solid tumors*
**作者**:Chen, X., et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向LILRB5的单克隆抗体,通过阻断其与HLA-G的相互作用,逆转肿瘤微环境中的T细胞抑制,增强抗肿瘤免疫反应。体外实验表明抗体可提升T细胞增殖和细胞因子分泌。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of LILRB5 recognition and its role in immune regulation*
**作者**:Liu, Y., et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析LILRB5与配体结合的分子结构,揭示其抑制性信号传导机制。研究进一步利用抗体阻断LILRB5.证明其在自身免疫疾病模型中可减轻炎症反应,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting LILRB5 in AML: A novel antibody therapy approach*
**作者**:Wang, H., et al.
**摘要**:针对急性髓系白血病(AML)中LILRB5的高表达,开发了人源化抗体HL-15.实验显示该抗体通过ADCC效应杀伤AML细胞,并抑制白血病干细胞自我更新,具有临床转化潜力。
---
(注:以上为模拟文献案例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“LILRB5 antibody”获取。)
LILRB5 (Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor B5), a member of the LILRB family, is an inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor expressed on immune cells such as monocytes, dendritic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. It belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in its cytoplasmic domain, enabling it to transmit suppressive signals upon ligand binding. LILRB5 primarily interacts with classical and non-classical MHC class I molecules (e.g., HLA-A, HLA-G), modulating immune responses to maintain tolerance and prevent excessive activation.
In the tumor microenvironment, LILRB5 is often exploited by cancer cells to evade immune surveillance. Overexpression of LILRB5 on exhausted T cells or myeloid cells can dampen antitumor immunity, promoting tumor progression. This mechanism has positioned LILRB5 as a promising therapeutic target, particularly in cancers with immune evasion phenotypes.
LILRB5-targeting antibodies are being developed to block its inhibitory signaling, thereby reactivating immune cell function. Preclinical studies suggest that anti-LILRB5 antibodies enhance T cell and NK cell-mediated tumor killing, synergizing with existing therapies like PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Additionally, LILRB5 isoforms (e.g., membrane-bound vs. soluble) may influence disease progression, necessitating isoform-specific therapeutic strategies. Ongoing research aims to elucidate its role in autoimmune disorders and infectious diseases, expanding its potential clinical applications.
×