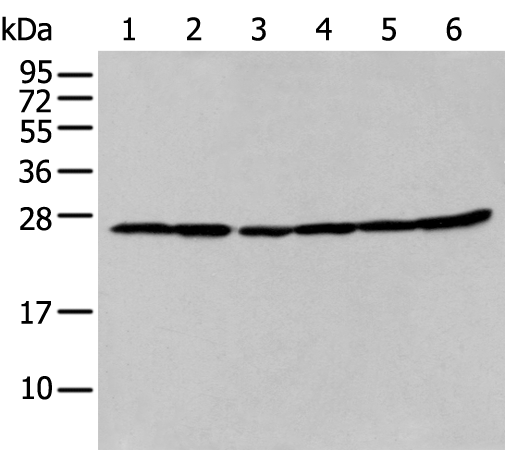
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABAD; CAMR; ERAB; HCD2; MHBD; HADH2; MRPP2; MRX17; MRX31; SCHAD; MRXS10; SDR5C1; 17b-HSD10; DUPXp11.22 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HSD17B10 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HSD17B10抗体的3篇参考文献示例:
1. **文献名称**:*HSD17B10 deficiency disrupts mitochondrial function and induces oxidative stress in neuronal cells*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用HSD17B10抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现HSD17B10缺失导致线粒体膜电位下降及活性氧(ROS)累积,提示其在神经元氧化应激中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*The role of 17β-HSD10 in Alzheimer's disease: Aβ interaction and neurotoxicity*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和免疫组化技术,作者证实HSD17B10抗体可特异性识别与β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)结合的HSD17B10.并揭示其在阿尔茨海默病中促进神经细胞凋亡的机制。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel mutation in HSD17B10 causes X-linked intellectual disability with altered mitochondrial morphology*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用HSD17B10抗体对患者成纤维细胞进行蛋白表达分析,发现特定突变导致酶活性丧失,并伴随线粒体形态异常,为X连锁智力障碍的分子机制提供了证据。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需以具体论文为准。)
The HSD17B10 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the multifunctional mitochondrial enzyme 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 (HSD17B10), also known as ERAB, ABAD, or MHBD. This protein plays diverse roles in steroid metabolism, neuroprotection, and mitochondrial function. It catalyzes the oxidation of steroids, including the conversion of estradiol to estrone, and participates in the catabolism of branched-chain amino acids and fatty acids. HSD17B10 is implicated in neurological disorders, particularly Alzheimer’s disease, as it interacts with amyloid-β peptide, potentially contributing to neuronal toxicity. Additionally, mutations in the HSD17B10 gene are linked to HSD10 disease, a rare X-linked neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability, seizures, and cardiomyopathy.
The HSD17B10 antibody enables researchers to detect and quantify this protein in various experimental settings, such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Its application aids in understanding tissue-specific expression, subcellular localization, and altered expression patterns in disease models. Validated antibodies are essential for distinguishing HSD17B10 from structurally similar enzymes, ensuring specificity in studies exploring its dual roles in metabolism and neurodegeneration. Both monoclonal and polyclonal variants are available, with selection depending on assay requirements. Researchers often use knockout controls or peptide blocking to confirm antibody specificity. Overall, the HSD17B10 antibody is vital for elucidating the protein’s pathophysiological mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
×