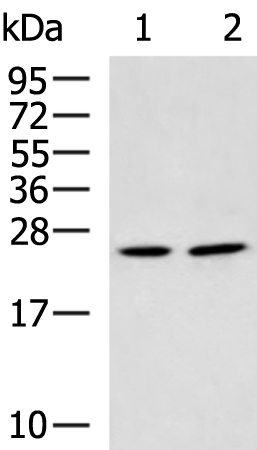
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
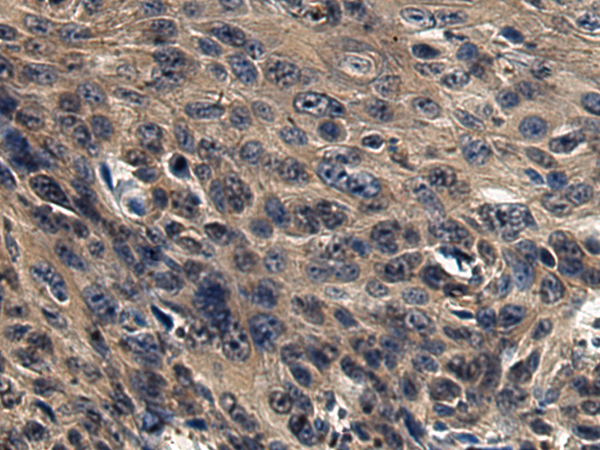
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCP-X; CGL-2; CSP-C; CTLA1; CTSGL2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GZMH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于GZMH(颗粒酶H)抗体的参考文献,涵盖其功能研究和应用:
1. **文献名称**: *"Granzyme H serum levels are associated with CD8+ T cell immunity in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma"*
**作者**: Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过开发特异性GZHM抗体,检测肝细胞癌患者血清中GZMH水平,发现其与CD8+ T细胞活性及患者预后显著相关,提示GZMH可能作为免疫治疗的潜在标志物。
2. **文献名称**: *"A novel monoclonal antibody against human granzyme H for functional characterization in cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated apoptosis"*
**作者**: Müller, L. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队报道了一种新型GZMH单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在流式细胞术和Western blot中的特异性,并证明其能有效阻断颗粒酶H介导的靶细胞凋亡,为免疫机制研究提供工具。
3. **文献名称**: *"Differential expression of granzyme H in human lymphocyte subsets identifies unique functional roles in inflammation"*
**作者**: Wang, Q. et al.
**摘要**: 通过GZHM抗体的免疫组化分析,揭示了颗粒酶H在NK细胞和Th1细胞亚群中的差异性表达,并发现其在慢性炎症疾病中调控细胞因子分泌的功能。
---
如需获取具体文献全文,建议通过PubMed或ResearchGate检索标题或作者。
Granzyme H (GZMH) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the function of GZMH, a serine protease in the granzyme family. Granzymes are primarily expressed in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells, where they contribute to immune defense by inducing apoptosis in virus-infected or tumorigenic cells. Unlike the well-characterized Granzyme B (GZMB), which cleaves caspases to trigger programmed cell death, GZMH exhibits distinct substrate specificity and enzymatic activity. It is thought to play a role in alternative cell death pathways or immune modulation, though its precise biological mechanisms remain less understood.
Research suggests GZMH may be involved in antiviral responses, particularly against herpesviruses and poxviruses, and its expression is upregulated in certain cancers, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammatory conditions. GZMH antibodies enable the detection of this protein in tissues or cells via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or flow cytometry, aiding investigations into its localization, expression patterns, and functional interactions. Recent studies also explore its potential as a biomarker for disease prognosis or therapeutic targeting. However, cross-reactivity with other granzymes and variability in antibody specificity require careful validation in experimental settings. Ongoing research aims to clarify GZMH's unique contributions to immune regulation and pathology.
×