| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
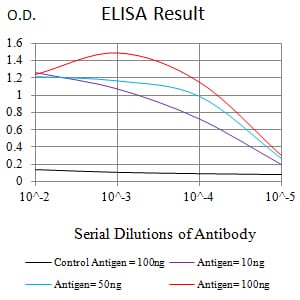
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APG10; APG10L; pp12616 |
| Entrez GeneID | 83734 |
| clone | 3F3C2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ATG10 (AA: 1-125) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CCR4抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Mogamulizumab (anti-CCR4) in ATL and PTCL*
**作者**: Ishida T. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究评估了抗CCR4单抗Mogamulizumab在复发/难治性成人T细胞白血病(ATL)和外周T细胞淋巴瘤(PTCL)中的疗效与安全性。结果显示,该抗体通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)显著抑制肿瘤进展,并延长患者生存期。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural basis for CCR4 recognition by a human antibody*
**作者**: Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜技术解析了人源化CCR4抗体与受体结合的分子机制,揭示了抗体特异性靶向CCR4 N端表位的关键结构域,为优化抗体药物设计提供了理论依据。
3. **文献名称**: *CCR4 blockade enhances immunotherapy in melanoma*
**作者**: Sugiyama D. et al.
**摘要**: 研究证明,抑制CCR4可减少肿瘤微环境中调节性T细胞(Treg)的浸润,增强抗PD-1疗法的效果。动物模型显示,联合CCR4抗体与免疫检查点抑制剂显著抑制黑色素瘤生长。
---
这些文献涵盖了临床治疗、结构机制及联合疗法等方向,反映了CCR4抗体在肿瘤免疫领域的多样化应用。
CCR4 (C-C chemokine receptor type 4) is a G protein-coupled receptor expressed on immune cells, including Th2 cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and certain malignancies. It binds chemokines CCL17 and CCL22. playing a key role in cell migration and immune regulation. In cancer, CCR4 is often overexpressed in aggressive T-cell lymphomas (e.g., adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma) and solid tumors, where it facilitates tumor cell trafficking and immune evasion by recruiting immunosuppressive Tregs into the tumor microenvironment.
Therapeutic CCR4 antibodies, such as mogamulizumab, are designed to target and block CCR4 signaling. Mogamulizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, received FDA approval in 2018 for relapsed/refractory mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome. It works via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), selectively depleting CCR4-positive malignant cells. However, CCR4 inhibition may also affect normal immune cells, potentially leading to autoimmune or infectious complications.
Research continues to explore CCR4's role in other diseases, including autoimmune disorders and HIV infection, where CCR4 serves as a co-receptor for viral entry. Challenges include optimizing specificity to minimize off-target effects and overcoming resistance mechanisms. Dual-targeting strategies and combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors are under investigation to enhance efficacy in both hematologic and solid cancers. CCR4 remains a promising but complex therapeutic target in immuno-oncology.
×