| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
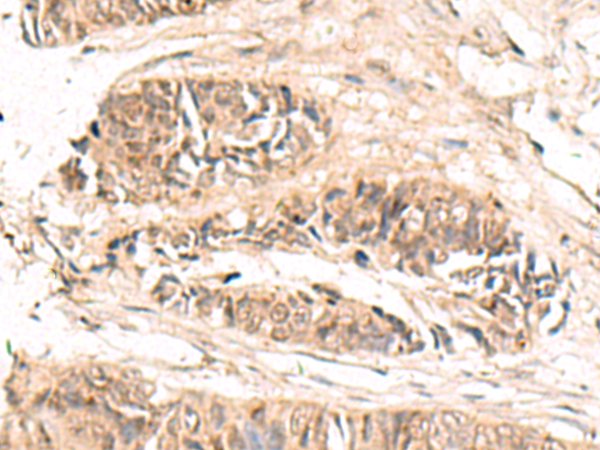
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GBD1; ICP3; MDR2; MDR3; PGY3; ABC21; MDR2/3; PFIC-3 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ABCB4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ABCB4抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
1. **"Characterization of a monoclonal antibody against human ABCB4 for detection of biliary phospholipid secretion defects"**
- **作者**: Delaunay JL, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究开发了一种特异性针对人ABCB4蛋白的单克隆抗体,用于评估胆汁中磷脂分泌异常相关的肝病(如进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症)。该抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证,可用于临床样本中ABCB4表达水平的定量分析。
2. **"ABCB4 deficiency promotes angiogenesis in cholestatic liver disease via VEGF signaling"**
- **作者**: Hoekstra LT, et al.
- **摘要**: 文章利用ABCB4基因敲除小鼠模型,通过免疫荧光和Western blot技术(使用ABCB4特异性抗体)证实ABCB4缺失导致血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)信号通路激活,进而加剧胆汁淤积性肝病的血管生成。
3. **"Immunohistochemical localization of ABCB4 in human liver tissue: implications for drug-induced liver injury"**
- **作者**: Stieger B, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究采用ABCB4抗体对正常和病变人类肝组织进行免疫组化分析,发现ABCB4在胆小管膜上的表达降低与药物性肝损伤相关,提示其可作为评估药物肝毒性的潜在生物标志物。
以上文献均涉及ABCB4抗体的实验应用,涵盖抗体开发、疾病机制及临床诊断方向。
ABCB4. a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, is encoded by the *ABCB4* gene and plays a critical role in hepatobiliary function. Expressed predominantly in the liver, it mediates the translocation of phosphatidylcholine (a major biliary phospholipid) across the canalicular membrane into bile, a process essential for protecting cholangiocytes from bile acid toxicity and maintaining bile homeostasis. Dysfunctional ABCB4 is linked to multiple cholestatic liver diseases, including progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3), intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), and low phospholipid-associated cholelithiasis (LPAC). These conditions often arise from mutations or reduced expression of ABCB4. leading to impaired phospholipid secretion, bile duct damage, and fibrosis.
ABCB4 antibodies are vital reagents for detecting and characterizing this transporter in research and diagnostics. They enable the visualization of ABCB4 expression patterns via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding studies on its regulation, interaction partners, and disease-associated alterations. Clinically, these antibodies support genetic testing by confirming protein deficiency in liver biopsies, guiding diagnosis of inherited cholestatic syndromes. Furthermore, they are instrumental in developing therapeutic strategies, such as gene therapy or pharmacological chaperones, to restore ABCB4 function. By elucidating ABCB4’s role in bile formation and pathology, these antibodies contribute to advancing precision medicine for cholestatic disorders.
×