| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
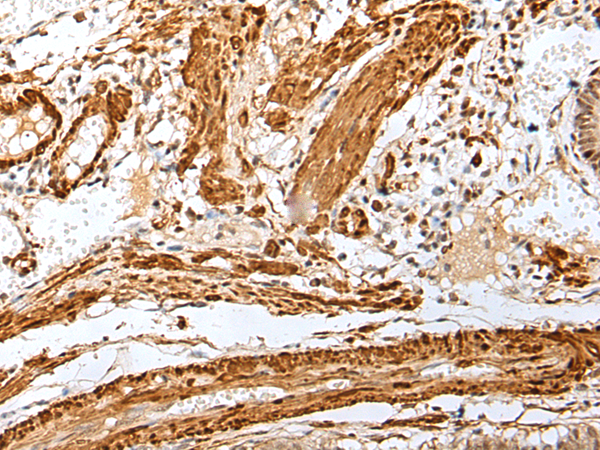
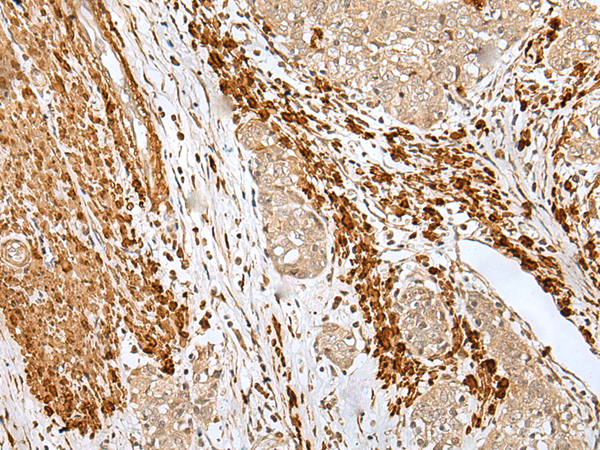
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PF-4; CXCL4; SCYB4 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human PF4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PF4抗体的3篇经典文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Antibodies to macromolecular platelet factor 4-heparin complexes in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia*
**作者**:Amiral, J., Bridey, F., Wolf, M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次揭示了肝素诱导的血小板减少症(HIT)患者体内存在针对血小板因子4(PF4)-肝素复合物的抗体,阐明了这些抗体通过激活血小板导致血栓形成的机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Clinical practice. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia*
**作者**:Arepally, G.M., Ortel, T.L.
**摘要**:综述了PF4抗体在HIT中的核心作用,强调其通过结合PF4-肝素复合物激活血小板和内皮细胞,导致血栓并发症,并讨论了诊断和替代抗凝治疗策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Laboratory testing for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia*
**作者**:Warkentin, T.E.
**摘要**:系统分析了PF4抗体检测(如ELISA和功能学方法)在HIT诊断中的价值,指出抗体滴度与临床严重程度相关,但需结合临床表现综合判断。
---
如需具体文献年份或补充更多研究,可进一步说明!
Platelet Factor 4 (PF4), a chemokine stored in platelet α-granules, plays roles in coagulation and inflammation. PF4 antibodies, particularly IgG class, are central to heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), a prothrombotic disorder triggered by heparin therapy. In HIT, heparin binds PF4. forming complexes that trigger IgG antibody production. These antibodies activate platelets via Fcγ receptors, causing thrombosis and platelet consumption.
Recently, PF4 antibodies gained attention in vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), a rare complication linked to adenoviral vector COVID-19 vaccines (e.g., AstraZeneca). Unlike HIT, VITT occurs without heparin exposure. Antibodies in VITT directly target PF4. inducing platelet activation and thrombosis through similar Fcγ receptor pathways, though the initial trigger remains unclear.
PF4 antibody detection involves ELISA (to identify anti-PF4/heparin antibodies) and functional assays (e.g., serotonin-release assay) to confirm platelet-activating capacity. However, not all PF4-reactive antibodies are pathogenic; clinical correlation is essential.
Research continues to explore why only some individuals develop pathogenic PF4 antibodies, focusing on genetic, immunological, and structural factors. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for improving diagnostics and therapies for antibody-mediated thrombotic disorders.
×