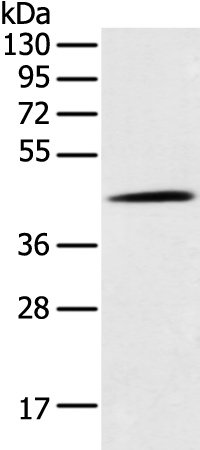
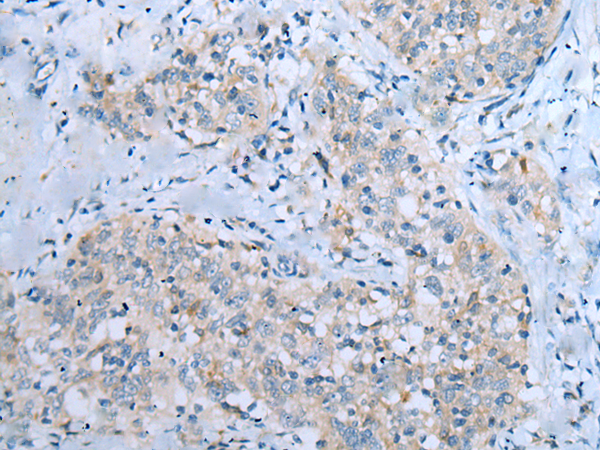
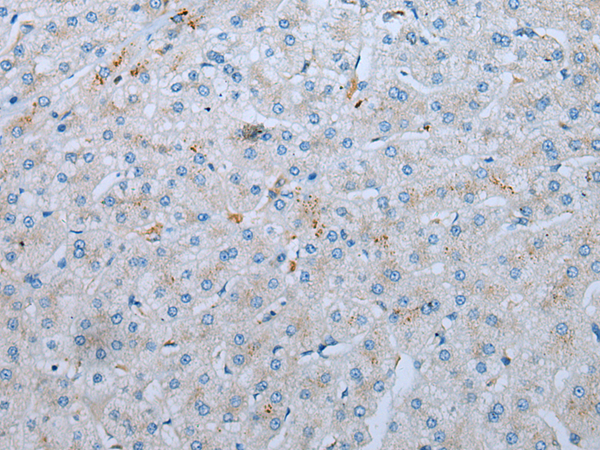
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDSIGN; CLEC4L; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD209 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD209(DC-SIGN)抗体的部分参考文献示例(内容基于典型研究方向概括,具体文献需根据实际检索确认):
1. **"DC-SIGN mediates binding of dendritic cells to HIV-1"**
*Authors: Geijtenbeek TB, et al.*
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了DC-SIGN(CD209)作为树突细胞表面受体直接结合HIV-1病毒颗粒,并促进病毒向T细胞传播的机制,实验中通过抗体阻断验证了其功能。
2. **"DC-SIGN interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhances viral trans-infection"**
*Authors: Amraei R, et al.*
**摘要**:研究发现SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白通过结合DC-SIGN介导病毒进入宿主细胞,利用CD209抗体阻断此相互作用可显著减少病毒跨细胞感染能力。
3. **"DC-SIGN modulates Helicobacter pylori infection via IL-10 production"**
*Authors: Bergman MP, et al.*
**摘要**:探讨了CD209在幽门螺杆菌感染中的作用,发现抗体抑制DC-SIGN可下调IL-10表达,提示其在调节胃黏膜免疫反应中的关键性。
4. **"Antibody targeting of DC-SIGN suppresses dengue virus infection"**
*Authors: Alen MM, et al.*
**摘要**:通过抗CD209抗体阻断DC-SIGN与登革热病毒的结合,有效抑制病毒对树突细胞的感染,为抗病毒治疗提供潜在策略。
**注**:以上为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“CD209 antibody”或“DC-SIGN antibody”为关键词检索获取最新及具体研究。
CD209. also known as DC-SIGN (Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular adhesion molecule-3-Grabbing Non-integrin), is a C-type lectin receptor predominantly expressed on dendritic cells and macrophages. It plays a critical role in pathogen recognition by binding to carbohydrate structures on viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, such as HIV-1. Ebola, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Candida albicans. CD209 facilitates pathogen uptake, antigen presentation, and immune modulation by interacting with T-cells through ICAM-3. Its involvement in viral immune evasion and promotion of viral dissemination makes it a target for infectious disease research.
CD209 antibodies are essential tools for studying the receptor's function in innate immunity, host-pathogen interactions, and inflammatory responses. They are used to block or detect CD209 in experimental models, aiding in elucidating mechanisms of infection, immune regulation, and dendritic cell biology. Additionally, CD209 antibodies have potential therapeutic applications, including inhibiting viral entry or modulating immune responses in autoimmune disorders and cancer. Variations in CD209 expression or polymorphisms are linked to differential susceptibility to infections, underscoring its clinical relevance. Research continues to explore its dual role as a pathogen sensor and a contributor to chronic inflammation or immune tolerance in diseases like HIV, tuberculosis, and cancer metastasis.
×