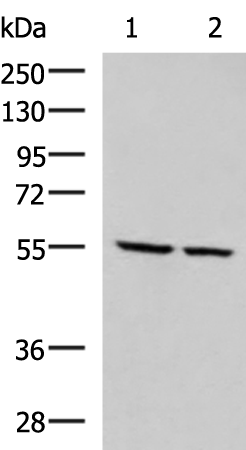
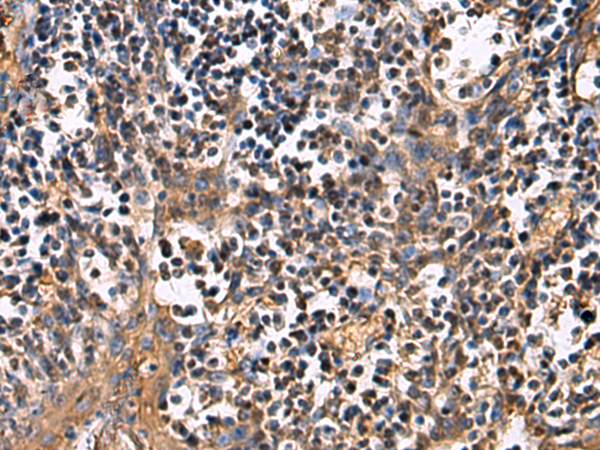
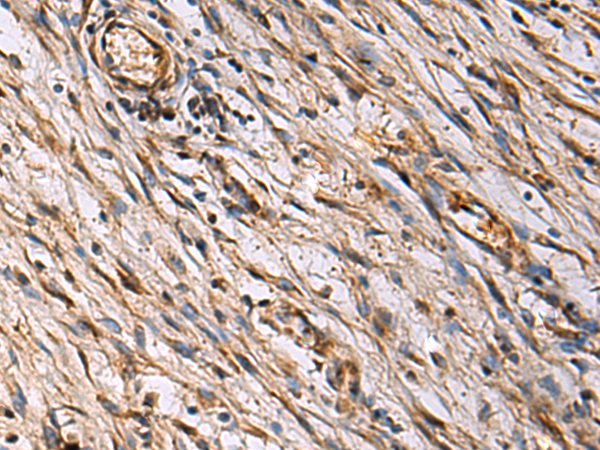
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | URBWD |
| WB Predicted band size | 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ECM1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于ECM1抗体的文献摘要概述,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *ECM1 regulates tumor metastasis and chemoresistance via the YAP signaling*
**作者**: Wang X et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了ECM1在乳腺癌中通过激活YAP信号通路促进肿瘤转移和化疗耐药。使用抗ECM1抗体阻断其功能可显著抑制小鼠模型中肿瘤细胞的侵袭性,并增强化疗敏感性,提示ECM1抗体在靶向治疗中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against ECM1 are linked to lipoid proteinosis pathogenesis*
**作者**: Hamada T et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次在脂质蛋白沉积症患者血清中检测到针对ECM1的自身抗体,证实其与皮肤和黏膜异常沉积直接相关。抗ECM1抗体的发现为疾病诊断和机制研究提供了新方向。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Targeting ECM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma with monoclonal antibody therapy*
**作者**: Li Y et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种靶向ECM1的单克隆抗体,体外实验显示其可抑制肝癌细胞增殖并诱导凋亡。动物实验中,抗体治疗显著降低肿瘤负荷,表明ECM1是肝癌治疗的潜在分子靶点。
---
**备注**:以上内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Web of Science检索(关键词:ECM1 antibody/therapeutic)。如需具体文献,建议查询近年肿瘤学或免疫学领域期刊。
The extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) is a secreted glycoprotein encoded by the *ECM1* gene, first identified in 1997. It plays a multifaceted role in tissue development, angiogenesis, and cell differentiation by interacting with components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and signaling pathways. ECM1 is expressed in various tissues, including skin, blood vessels, and bone, and exists in multiple isoforms (e.g., ECM1a, ECM1b) due to alternative splicing. Dysregulation of ECM1 has been implicated in pathological conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and skin diseases.
Antibodies targeting ECM1 have emerged as critical tools in research and diagnostics. In oncology, ECM1 overexpression correlates with tumor progression and metastasis in cancers like hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer, making ECM1 antibodies valuable for detecting tumor biomarkers. In dermatology, anti-ECM1 autoantibodies are linked to lichen sclerosus and lipoid proteinosis, aiding in disease diagnosis. Additionally, ECM1 antibodies are used to study the protein's role in angiogenesis, particularly its interaction with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathways. Therapeutic applications are also being explored, including blocking ECM1 to inhibit tumor growth or modulate immune responses. However, challenges remain in understanding isoform-specific functions and optimizing antibody specificity for clinical use.
×