| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
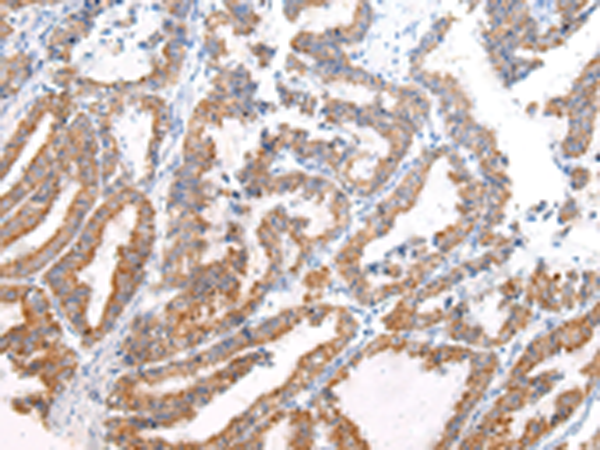
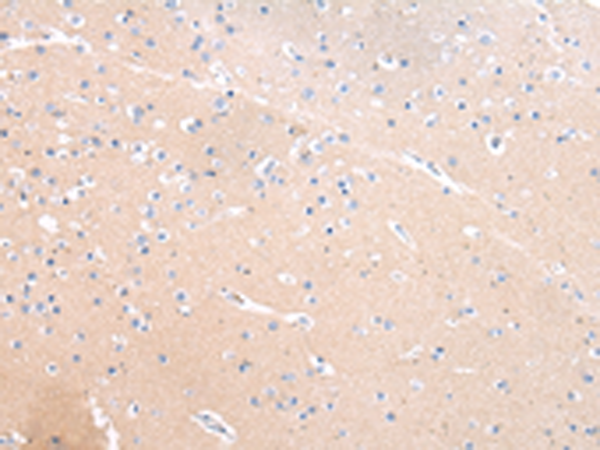
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLI; AAG4; APOJ; CLU1; CLU2; KUB1; SGP2; APO-J; SGP-2; SP-40; TRPM2; TRPM-2; NA1/NA2 |
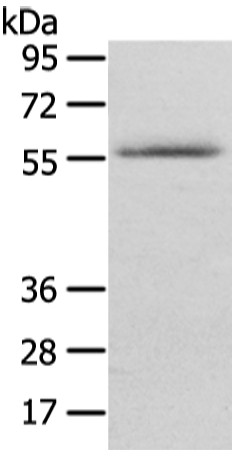
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CLU |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLU(Clusterin)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Clusterin promotes amyloid plaque formation and is critical for neuritic toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease*
**作者**:DeMattos, R.B. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化及抗体标记技术,发现Clusterin与β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)在阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中共定位,并证明其通过结合Aβ促进淀粉样斑块形成,加剧神经元毒性。
2. **文献名称**:*Clusterin as a therapeutic target for prostate cancer*
**作者**:July, L.V. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用CLU特异性抗体检测前列腺癌细胞系及患者组织样本,发现Clusterin在癌症进展中高表达,并通过抗体阻断实验证明抑制CLU可增强化疗敏感性,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of Clusterin in stress-induced apoptosis and carcinogenesis*
**作者**:Trougakos, J.P. et al.
**摘要**:综述了Clusterin在细胞应激反应中的双重作用,包括抗凋亡和促凋亡功能,并总结了基于CLU抗体的实验方法在解析其分子机制及癌症治疗中的应用。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需核对具体来源及准确性。)
**Background of CLU Antibodies**
Clusterin (CLU), also known as apolipoprotein J, is a multifunctional glycoprotein ubiquitously expressed in tissues and bodily fluids. It plays roles in apoptosis, cell survival, protein homeostasis, and immune regulation. Structurally, CLU exists as a secreted heterodimeric protein formed by disulfide-linked α and β subunits, generated through proteolytic cleavage of a single precursor. Its chaperone-like activity aids in stabilizing misfolded proteins, facilitating their clearance or aggregation, which links CLU to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, where it interacts with amyloid-β plaques.
CLU is implicated in cancer, exhibiting context-dependent roles as either a tumor suppressor or promoter. It contributes to treatment resistance by modulating apoptosis, DNA repair, and cell stress responses. In age-related macular degeneration (AMD), CLU gene variants are associated with disease risk, highlighting its role in extracellular matrix regulation.
CLU antibodies are critical tools for detecting CLU expression and function in research and diagnostics. They enable the study of CLU’s dual roles in disease via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Therapeutic strategies targeting CLU, including monoclonal antibodies, are under exploration to modulate its activity in cancer and neurodegeneration. Research on CLU continues to unravel its complex biology, offering potential biomarkers and therapeutic avenues for diverse pathologies.
×