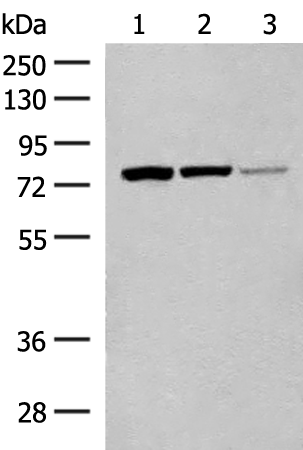
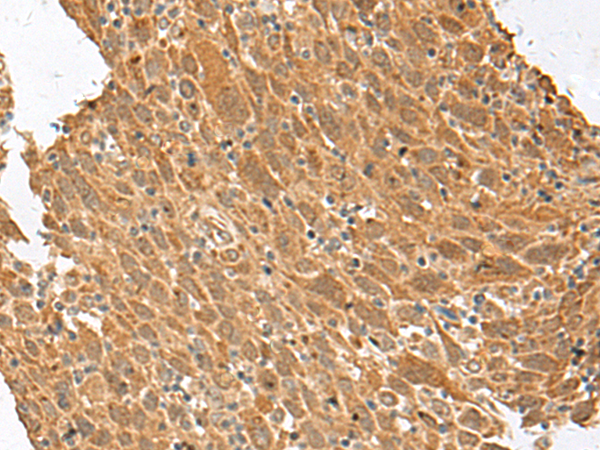
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HNF1; LFB1; TCF1; MODY3; TCF-1; HNF-1A; IDDM20 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HNF1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HNF1A抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*HNF1A Antibodies as a Marker of Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults*
**作者**:Hawa MI, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了HNF1A抗体在成人迟发性自身免疫糖尿病(LADA)中的诊断价值,发现部分患者血清中存在针对HNF1A的自身抗体,可能与β细胞功能进行性丧失相关,提示其作为糖尿病分型的潜在生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1α in Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary Biliary Cholangitis*
**作者**:Muratori P, et al.
**摘要**:研究分析了HNF1A抗体在自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)和原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)患者中的表达,发现HNF1A抗体与特定肝病亚型相关,可能参与肝脏自身免疫反应的病理机制。
3. **文献名称**:*HNF1A Mutations and Autoantibodies in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)*
**作者**:Ellard S, et al.
**摘要**:该文献指出,尽管MODY主要由HNF1A基因突变引起,但少数患者出现HNF1A抗体,提示遗传缺陷与自身免疫反应的潜在交叉,可能影响糖尿病的临床表现和治疗反应。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际发表情况需根据具体数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。若需真实文献,建议使用关键词“HNF1A antibodies”或“anti-HNF1A”在学术平台进一步查询。
HNF1A (Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1 Alpha) is a transcription factor encoded by the *HNF1A* gene, primarily expressed in the liver, pancreas, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. It plays a critical role in regulating tissue-specific gene expression, particularly genes involved in glucose metabolism, insulin secretion, and pancreatic β-cell function. Mutations in *HNF1A* are linked to maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3), a monogenic form of diabetes characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance and early-onset hyperglycemia.
Antibodies targeting HNF1A are essential tools in research and diagnostics. In research, they are used to study HNF1A's expression patterns, localization, and interactions with DNA or other proteins, aiding in understanding its role in development and disease. Clinically, HNF1A antibodies may assist in identifying autoimmune responses in rare cases of autoimmune diabetes or evaluating tissue-specific HNF1A dysfunction. However, unlike diabetes-associated autoantibodies (e.g., GAD65 or IA-2), HNF1A antibodies are not routinely used for diabetes classification. Instead, genetic testing remains the gold standard for confirming *HNF1A*-related MODY. Recent studies also explore HNF1A’s involvement in cancer and renal diseases, expanding the scope of its antibody applications. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to structural similarities with HNF1B. Overall, HNF1A antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling molecular pathways and advancing precision medicine for metabolic disorders.
×