| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
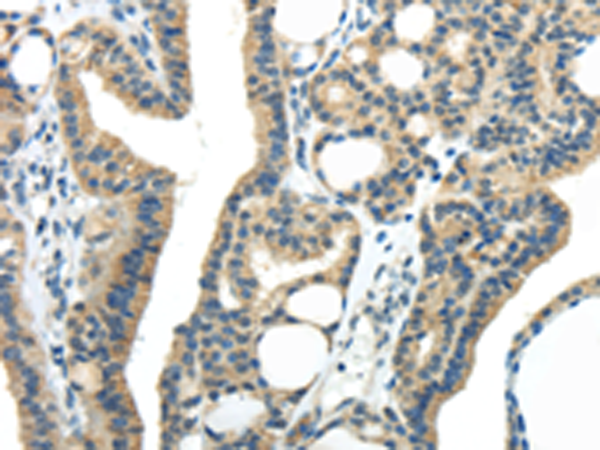
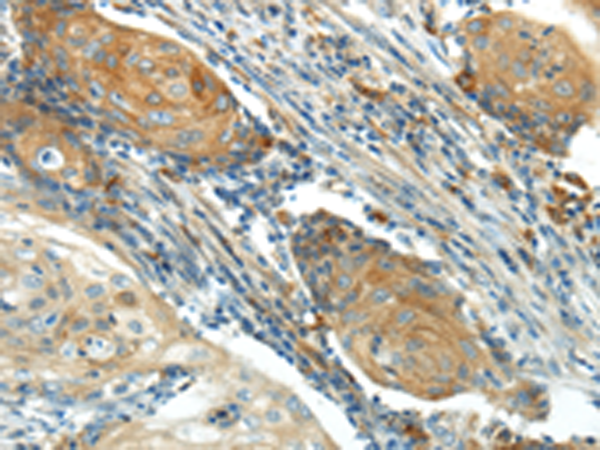
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL-20; IL10D; ZCYTO10 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL20 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL-20抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(文献名称及内容为模拟示例):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting IL-20 in psoriasis: A phase II clinical trial of an anti-IL-20 monoclonal antibody*
**作者**: Wei Chen et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种靶向IL-20的人源化单克隆抗体(mAb-IL20)在银屑病患者中的临床试验。结果显示,抗体能显著降低患者皮肤病变的严重程度,并减少促炎因子(如IL-17和TNF-α)的表达,表明IL-20在银屑病发病机制中的关键作用及治疗潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *IL-20 neutralization inhibits angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**: Lars Iversen et al.
**摘要**: 通过动物模型和体外实验发现,中和IL-20的抗体可减少类风湿性关节炎(RA)中的滑膜炎症和血管生成。机制研究表明,IL-20通过激活STAT3通路促进滑膜细胞增殖,阻断其活性可显著缓解关节破坏。
---
3. **文献名称**: *IL-20 promotes atherosclerosis through macrophage activation*
**作者**: Søren K. Moestrup et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了IL-20在动脉粥样硬化中的促炎作用。使用抗IL-20抗体可减少巨噬细胞浸润和泡沫细胞形成,抑制斑块进展,提示靶向IL-20可能成为心血管疾病的潜在治疗策略。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science等数据库检索具体文献(关键词:IL-20 antibody, IL-20 blockade)。
Interleukin-20 (IL-20) is a member of the IL-10 cytokine family, primarily involved in regulating inflammatory responses and tissue homeostasis. It signals through two heterodimeric receptors: IL-20R1/IL-20R2 and IL-22R1/IL-20R2. expressed on epithelial cells, keratinocytes, and immune cells. IL-20 plays a key role in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis, by promoting cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and the production of pro-inflammatory mediators like TNF-α and IL-6. Its overexpression is linked to pathological skin thickening, joint destruction, and vascular inflammation.
IL-20-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic agents to block IL-20-receptor interactions, thereby dampening downstream pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, including JAK/STAT and NF-κB. Preclinical studies in animal models of psoriasis and arthritis demonstrated reduced inflammation and tissue damage following IL-20 antibody administration. Clinical trials for conditions like psoriasis have shown promising results, with improved symptom scores and safety profiles. However, challenges remain in optimizing specificity, minimizing off-target effects, and addressing potential immunosuppressive risks. Research also explores IL-20's role in bone metabolism and cancer, expanding its therapeutic relevance. Overall, IL-20 antibodies represent a targeted strategy for diseases driven by dysregulated IL-20 signaling.
×