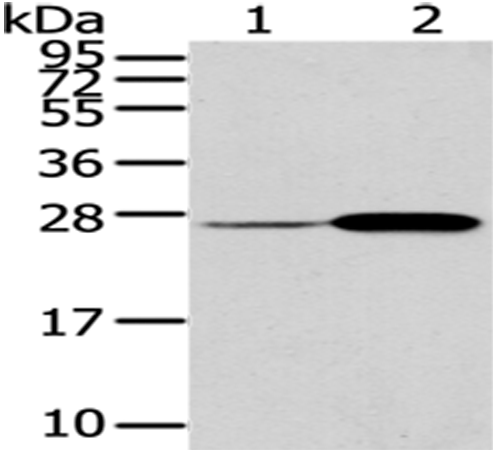
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IGA; MB-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD79A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD79A抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **《CD79A mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma》**
- 作者:Schmitz R et al.
- 摘要:该研究通过全基因组测序发现,弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)中存在高频的CD79A基因突变(约20%),突变导致BCR信号通路异常激活,提示CD79A抗体可作为靶向治疗及预后评估的生物标志物。
2. **《Targeting B-cell receptor signaling in lymphoma through anti-CD79A antibody-drug conjugates》**
- 作者:Polson AG et al.
- 摘要:研究开发了一种靶向CD79A的抗体药物偶联物(ADC),在非霍奇金淋巴瘤模型中显示显著抗肿瘤活性,表明CD79A抗体通过特异性结合并释放细胞毒素,可有效抑制B细胞恶性肿瘤增殖。
3. **《CD79A expression distinguishes chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma from other low-grade B-cell lymphomas》**
- 作者:Kussick SJ et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫组化分析发现,CD79A抗体在慢性淋巴细胞白血病/小淋巴细胞淋巴瘤(CLL/SLL)中呈现特异性弱表达模式,为鉴别低级别B细胞淋巴瘤亚型提供了重要诊断依据。
4. **《BCR signaling inhibition through anti-CD79A antibodies induces apoptosis in B-cell malignancies》**
- 作者:Young RM et al.
- 摘要:研究证明阻断CD79A介导的BCR信号通路可诱导B细胞肿瘤细胞凋亡,CD79A抗体通过抑制下游NF-κB和PI3K通路发挥治疗作用,为开发新型免疫疗法奠定基础。
以上文献涵盖了CD79A抗体在分子机制、靶向治疗、诊断分型及信号通路调控中的关键研究进展。
CD79a antibody targets the CD79a protein, a critical component of the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex. CD79a, encoded by the *CD79A* gene, pairs with CD79b to form a heterodimer that non-covalently associates with membrane-bound immunoglobulins (IgM/IgD) on B cells. This complex is essential for BCR signaling, which regulates B-cell development, activation, and antigen presentation. CD79a contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) in its cytoplasmic domain, enabling signal transduction upon antigen binding and promoting B-cell survival and differentiation.
CD79a antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to identify B-cell lineages. In clinical pathology, they help detect B-cell malignancies (e.g., B-cell lymphomas, leukemias) by selectively labeling malignant B cells. Additionally, CD79a expression is retained in most B-cell cancers, even when surface immunoglobulin is lost, making it a reliable marker for classification. In therapeutics, CD79a-targeting strategies, such as antibody-drug conjugates or bispecific antibodies, are under investigation to modulate BCR signaling or deliver cytotoxic agents directly to B cells in autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Research on CD79a also explores its role in autoimmune disorders, as aberrant BCR signaling contributes to conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Mutations in *CD79A* are linked to immunodeficiency disorders, highlighting its importance in immune function. Overall, CD79a antibodies serve as vital tools for understanding B-cell biology and developing targeted therapies.
×