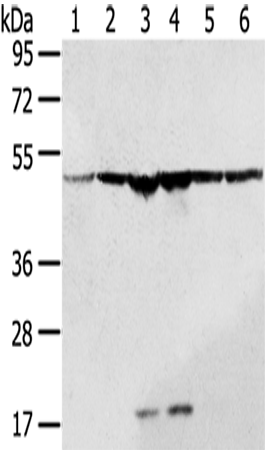
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
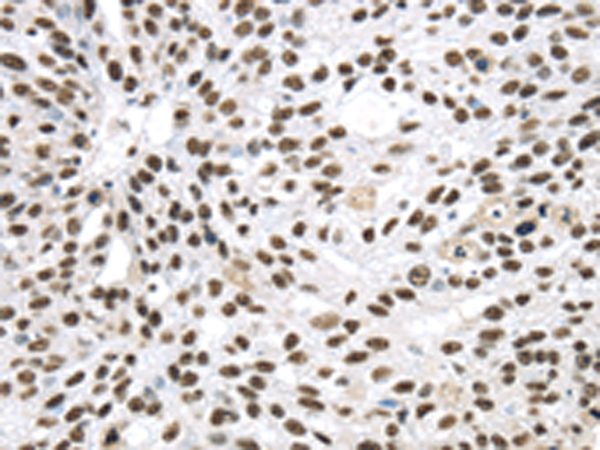
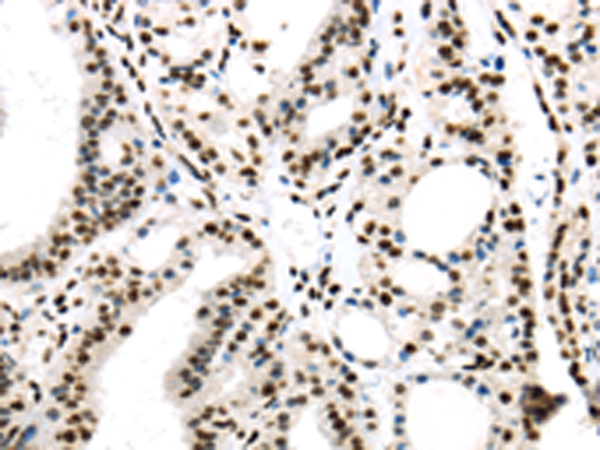
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BAT1; UAP56; D6S81E |
| WB Predicted band size | 49 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human DDX39B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于DDX39B抗体的文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
1. **"DDX39B interacts with the influenza virus NS1 protein and is essential for viral RNA synthesis"**
- **作者**: Wang S, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究利用DDX39B特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现DDX39B与流感病毒NS1蛋白相互作用,并通过调控病毒RNA的剪接和转运促进病毒复制。抗体验证了其在宿主-病毒互作中的关键作用。
2. **"Autoantibodies against DDX39B in systemic lupus erythematosus"**
- **作者**: Li Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过ELISA和Western blot分析,研究发现系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在抗DDX39B的自身抗体,提示DDX39B可能作为自身抗原参与SLE的发病机制。研究中使用的多克隆抗体被用于检测患者样本中的抗原反应性。
3. **"DDX39B regulates mRNA export and is required for embryonic development"**
- **作者**: Kang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过CRISPR/Cas9敲除结合DDX39B抗体的免疫荧光染色,揭示该蛋白在胚胎干细胞mRNA出核转运中的功能,并证明其缺失导致胚胎发育异常。抗体在亚细胞定位研究中发挥关键作用。
4. **"The RNA helicase DDX39B promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation"**
- **作者**: Chen L, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用DDX39B抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在结直肠癌组织中高表达,并通过激活Wnt通路促进肿瘤转移。抗体被用于评估临床样本中DDX39B的蛋白表达水平与预后的相关性。
(注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需核实原文信息及数据库收录情况。)
DDX39B, also known as BAT1 or UAP56. is a member of the DEAD-box RNA helicase family, which plays critical roles in RNA metabolism, including pre-mRNA splicing, nuclear export, and translation. This ATP-dependent enzyme facilitates the remodeling of RNA-protein complexes and is essential for mRNA processing and genome stability. Dysregulation of DDX39B has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Its involvement in immune response regulation, particularly in MHC class II antigen presentation, further underscores its biological significance.
Antibodies targeting DDX39B are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional mechanisms. They enable researchers to investigate DDX39B's role in RNA splicing machinery, its interaction with cofactors like ALYREF, and its impact on cellular processes such as proliferation and apoptosis. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation. In clinical contexts, DDX39B antibodies aid in exploring its potential as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker in cancers, where its overexpression is often associated with tumor progression. Additionally, they help elucidate DDX39B's interplay with viral infections, as some viruses exploit its RNA-binding activity for replication. The development of high-specificity, validated DDX39B antibodies remains crucial for advancing both basic research and therapeutic targeting strategies.
×