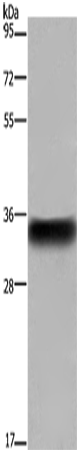
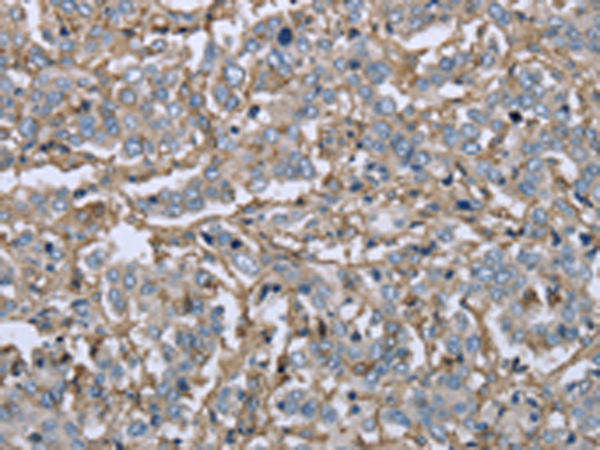
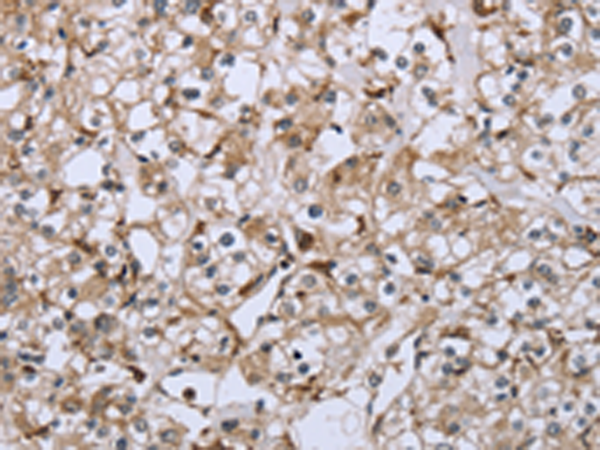
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD32; FCG2; CD32B; FCGR2; IGFR2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FCGR2B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FCGR2B抗体的3-4篇代表性文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses"*
**作者**: Jeffrey V. Ravetch and Falk Nimmerjahn
**摘要**: 该综述系统探讨了Fcγ受体家族(包括抑制性受体FCGR2B)在免疫调控中的作用,指出FCGR2B通过传递抑制信号平衡B细胞和髓系细胞的激活,对维持免疫耐受和防止自身免疫反应至关重要。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Role of FcγRIIB polymorphism in autoimmune disease"*
**作者**: Chieko Kyogoku et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过基因关联分析发现,FCGR2B的启动子区或编码区多态性(如I232T突变)与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)等自身免疫疾病的易感性相关,功能缺失可能导致B细胞过度活化。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Enhancing cancer immunotherapy by blocking the inhibitory FcγRIIB"*
**作者**: Mark J. Smyth et al.
**摘要**: 实验证明,在抗肿瘤单克隆抗体(如抗CD20)治疗中,阻断FCGR2B可增强巨噬细胞和自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)的抗体依赖性细胞吞噬(ADCP)作用,显著提升小鼠模型的肿瘤清除效果。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Structural basis of FcγRIIB regulation in antibody therapy"*
**作者**: Peter Sondermann et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了FCGR2B与IgG-Fc段的复合物结构,揭示了其抑制性信号转导的分子机制,为设计靶向FCGR2B的工程化抗体(如增强/削弱结合)提供了结构依据。
---
这些文献涵盖了FCGR2B的核心功能、疾病关联、治疗应用及结构机制,可作为相关研究的参考。
Fc gamma receptor IIB (FCGR2B) is an inhibitory immune receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on B cells and myeloid cells. It plays a critical role in modulating immune responses by dampening activation signals upon binding to immune complexes via its intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM). This negative regulation helps maintain immune tolerance and prevent hyperactivation, making FCGR2B a key checkpoint in autoimmune diseases, infections, and cancer.
FCGR2B-targeting antibodies have gained attention for therapeutic and research applications. In autoimmune disorders like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), enhancing FCGR2B signaling could suppress pathogenic antibody production. Conversely, in cancer immunotherapy, blocking FCGR2B may counteract its inhibitory effects on effector cells (e.g., macrophages, NK cells), potentially enhancing antitumor activity. However, developing selective antibodies is challenging due to high homology with activating Fc receptors (e.g., FCGR2A).
Genetic polymorphisms in FCGR2B are linked to disease susceptibility, particularly in SLE and malaria. For example, a T→I232 mutation disrupts its function, correlating with autoimmune risk. Research tools like anti-FCGR2B monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clone AT10) are widely used to study receptor expression, signaling crosstalk, and immune cell regulation. Ongoing efforts focus on engineering bispecific antibodies or fusion proteins to fine-tune FCGR2B activity, balancing efficacy and safety in clinical applications.
×