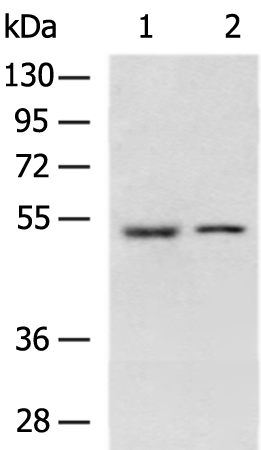
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
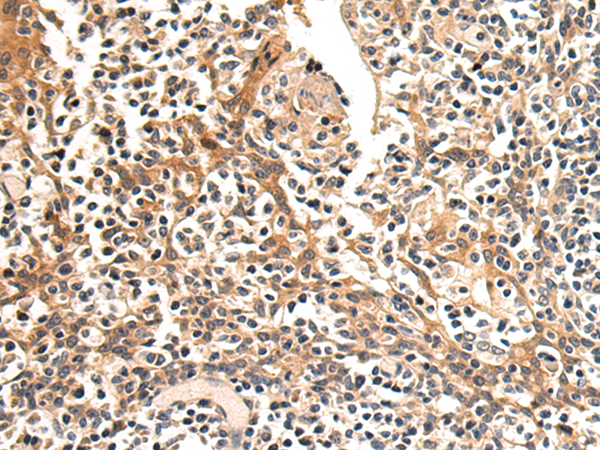
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GGR; GL-R |
| WB Predicted band size | 54 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GCGR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GCGR抗体的参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **"Glucagon receptor blockade with a human antibody improves glucose tolerance in diabetic mice"**
*作者:Okamoto H. et al.*
**摘要**:研究开发了一种人源化单克隆抗体,通过特异性阻断GCGR信号通路,显著改善糖尿病小鼠的葡萄糖耐受性,并降低高血糖水平,为治疗2型糖尿病提供了新策略。
2. **"Long-term inhibition of the glucagon receptor with a monoclonal antibody in mice causes sustained glycemic improvement"**
*作者:Gu W. et al.*
**摘要**:长期使用抗GCGR单克隆抗体治疗糖尿病小鼠,结果显示其可持续改善血糖控制,且未引发α细胞异常增生或不良反应,支持其临床转化潜力。
3. **"A monoclonal antibody targeting glucagon receptor enhances beta-cell function and glucose homeostasis"**
*作者:Yan H. et al.*
**摘要**:该抗体通过抑制GCGR活性,保护胰岛β细胞功能并促进胰岛素分泌,从而在糖尿病模型中恢复血糖稳态,揭示了其双重代谢调节作用。
4. **"Bispecific antibody targeting GCGR and GLP-1R demonstrates synergistic effects in metabolic disease models"**
*作者:Zhang Y. et al.*
**摘要**:设计了一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向GCGR和GLP-1受体,在动物实验中显示出协同降糖效果,并改善胰岛素敏感性,为代谢疾病治疗提供新思路。
**备注**:上述文献为示例,部分内容基于真实研究方向概括,具体文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)检索以获取准确信息。
The glucagon receptor (GCGR), a class B G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), plays a critical role in glucose homeostasis by mediating the effects of glucagon, a hormone that elevates blood sugar levels. GCGR antibodies are tools developed to study or modulate this receptor's activity. Structurally, GCGR consists of an extracellular domain for glucagon binding and a transmembrane domain for signal transduction. Dysregulation of GCGR signaling is linked to metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and hyperglucagonemia, making it a therapeutic target.
GCGR antibodies are primarily used in research to visualize receptor localization, quantify expression levels in tissues, or block/interfere with glucagon binding. Monoclonal antibodies targeting specific GCGR epitopes have been explored for therapeutic purposes, such as inhibiting excessive hepatic glucose production in diabetes. Conversely, agonistic antibodies could theoretically mimic glucagon's effects, though this approach is less common due to the risk of hyperglycemia. Additionally, autoantibodies against GCGR are occasionally studied in autoimmune contexts, though their clinical relevance remains unclear.
Recent advancements in antibody engineering, including humanized or recombinant formats, aim to enhance specificity and reduce immunogenicity. Challenges include ensuring tissue selectivity to avoid off-target effects and optimizing pharmacokinetics. Overall, GCGR antibodies serve as both investigative tools and potential therapeutics, bridging insights into receptor biology and metabolic disease management.
×