| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
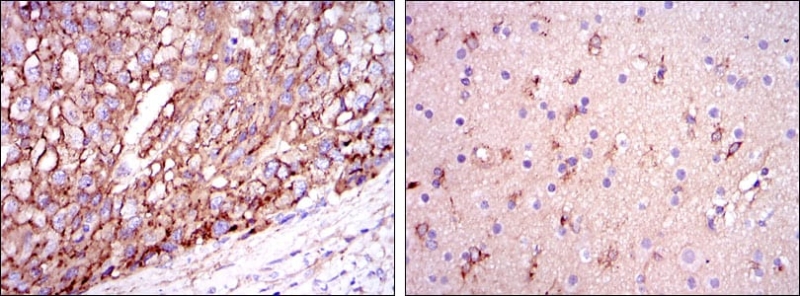
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
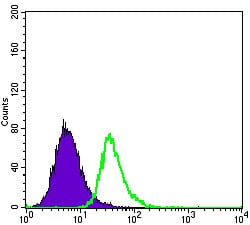
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
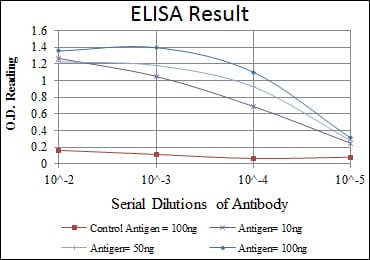
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AD2; LPG; LDLCQ5; MGC1571 |
| Entrez GeneID | 348 |
| clone | 1H4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ApoE expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MR1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Recognition of vitamin B metabolites by mucosal-associated invariant T cells*
**作者**:D. B. Moody, L. Lepenies, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了MR1分子通过呈递微生物代谢的维生素B衍生物抗原来激活MAIT细胞的机制,并开发了特异性MR1单克隆抗体用于阻断MR1-抗原复合物的形成,为研究MAIT细胞免疫应答提供了工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-MR1 monoclonal antibodies cross-react with human MHC class I molecules*
**作者**:J. McCluskey, A. G. Brooks, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种新型抗MR1抗体的生成,但发现其可能与经典MHC-I分子存在交叉反应,提示开发MR1抗体时需严格验证特异性,以避免在免疫检测或治疗中产生脱靶效应。
---
3. **文献名称**:*MR1-restricted T cells in cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:D. P. Fairlie, M. J. Eckle
**摘要**:该文献探讨了利用MR1抗体靶向肿瘤细胞表面MR1分子的策略,通过激活或抑制MAIT细胞功能来增强抗肿瘤免疫反应,为癌症免疫治疗提供了新思路。
---
如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以标题/作者关键词检索获取全文。
MR1 antibodies target the MHC class I-related molecule MR1. a highly conserved antigen-presenting protein that plays a unique role in mucosal immunity. Discovered in the 1990s, MR1 gained prominence for its ability to present microbial vitamin B2 (riboflavin) precursor derivatives to mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, a subset of innate-like T cells abundant in human blood and mucosal tissues. Unlike classical MHC molecules, MR1 is non-polymorphic and does not require antigen processing, instead binding small molecule metabolites derived from bacterial and fungal pathways. This interaction activates MAIT cells, triggering rapid immune responses against pathogens.
MR1-specific antibodies, such as the widely used clone 26.5. have become critical tools for studying MR1 biology. These antibodies block MR1-antigen presentation, enabling functional studies of MAIT cell activation and MR1-dependent immune regulation. Recent research explores MR1's therapeutic potential, with antibodies being developed to modulate MR1 in cancer immunotherapy (e.g., enhancing tumor antigen visibility) or autoimmune diseases (e.g., suppressing pathogenic T cell activation). Additionally, MR1 tetramers loaded with antigenic ligands allow precise tracking of MAIT cells in health and disease. The conservation of MR1 across mammals underscores its fundamental role in bridging innate and adaptive immunity, making it a compelling target for translational research.
×