| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
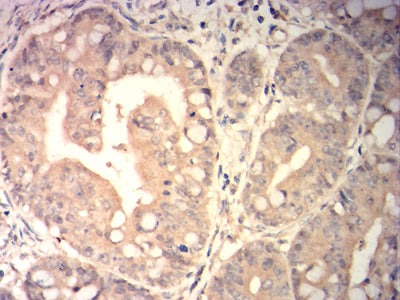
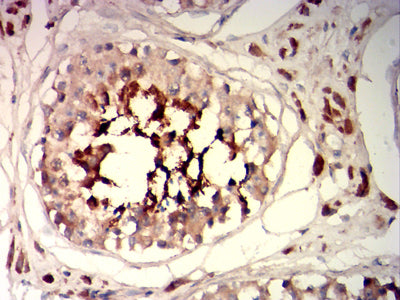
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
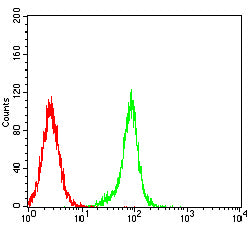
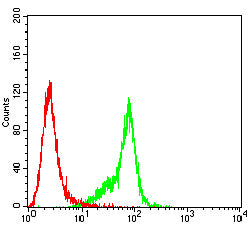
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
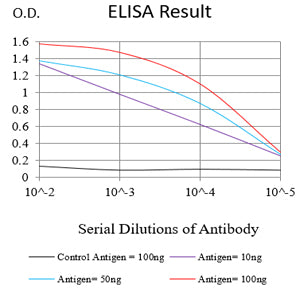
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT22; SPA17; SP17-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 53340 |
| clone | 3G9F3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 17.4 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SP17 (AA: 1-152) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于SP17抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*Sperm protein 17 is expressed in human nervous system tumors*
**作者**:D'anca M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化实验证实SP17蛋白在神经胶质瘤等神经系统肿瘤中异常表达,并利用特异性抗体检测其定位,提示SP17可能作为神经肿瘤的潜在生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Immunotherapeutic targeting of SP17 in multiple myeloma*
**作者**:Lim SH, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了针对SP17的单克隆抗体,体外实验显示其可介导多发性骨髓瘤细胞的抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC),为SP17靶向免疫治疗提供实验依据。
3. **文献名称**:*SP17 as a tumor-associated antigen in ovarian cancer*
**作者**:Fusi A, Dudas J.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和流式细胞术验证SP17在卵巢癌细胞系中的高表达,使用特异性抗体阻断SP17可抑制癌细胞迁移,提示其参与肿瘤转移通路。
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对最新研究。
SP17 (Sperm Protein 17) is a testis-specific protein first identified in spermatozoa, where it plays a role in sperm-egg interaction by binding to zona pellucida glycoproteins. Structurally, it contains a conserved N-terminal heparin-binding domain and a C-terminal region homologous to the RFC (Recombination Factor C) family. While primarily expressed in germ cells, SP17 has been detected ectopically in various cancers, including multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, and squamous cell carcinomas, suggesting potential oncogenic roles. Its aberrant expression in malignancies has been linked to epigenetic dysregulation, particularly hypomethylation of promoter regions.
SP17 antibodies have emerged as valuable tools for both research and clinical applications. In diagnostics, they help detect SP17 overexpression in tumor tissues or serum, aiding cancer subtyping and monitoring. Therapeutically, SP17 is investigated as a target for immunotherapy due to its cancer-specific expression pattern. Preclinical studies explore SP17-directed CAR-T cells and antibody-drug conjugates, showing reduced tumor burden in xenograft models. However, challenges persist, including heterogeneous SP17 expression across tumors and potential off-target effects in males due to residual testicular expression. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity and evaluating combinatorial approaches with checkpoint inhibitors to enhance anti-tumor efficacy.
×