| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
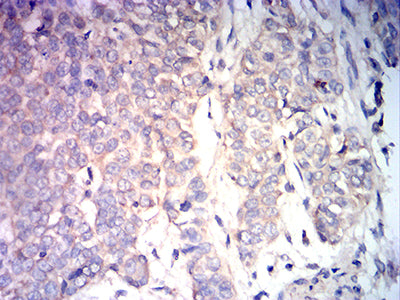
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
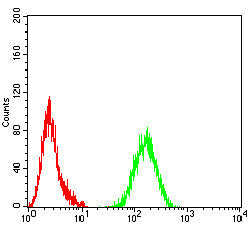
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
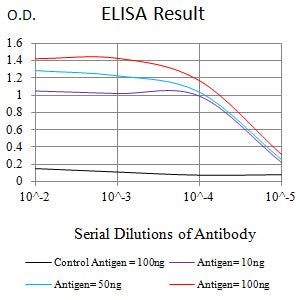
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCL2L4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 581 |
| clone | 2D8H2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BAX expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于BAX抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要整理如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Bax and Bcl-2 interactions in apoptosis*
**作者**:Oltvai, Z.N., Milliman, C.L., Korsmeyer, S.J.
**摘要内容**:
该研究通过免疫沉淀和Western blot技术,使用BAX特异性抗体验证了BAX与抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2之间的相互作用。结果表明,两者比例调控细胞对凋亡信号的敏感性,为凋亡通路研究提供了关键实验依据。
2. **文献名称**:*Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis*
**作者**:Wolter, K.G., Hsu, Y.T., Smith, C.L., Nechushtan, A., Xi, X.G., Youle, R.J.
**摘要内容**:
利用BAX抗体进行免疫荧光和亚细胞定位分析,揭示了BAX在凋亡过程中从细胞质向线粒体迁移的机制。研究证实BAX构象变化触发线粒体膜通透性改变,导致细胞色素C释放。
3. **文献名称**:*BAX is required for apoptosis in response to oncogenic stress*
**作者**:Scopa, C.D., Vagianos, C., Zolota, V., et al.
**摘要内容**:
通过免疫组化(使用BAX抗体)分析结直肠癌组织样本,发现BAX表达缺失与肿瘤细胞凋亡抑制相关。研究强调BAX在癌基因应激下诱导凋亡的必要性,为癌症治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
这些文献均涉及BAX抗体的实验应用,涵盖蛋白互作、亚细胞定位及疾病模型研究,可供相关领域参考。如需具体细节,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库查询原文。
The BAX antibody is a crucial tool in apoptosis research, targeting the Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX), a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. BAX plays a pivotal role in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), a key step in intrinsic apoptosis. Inactive BAX resides in the cytosol but undergoes conformational activation upon apoptotic stimuli, translocating to mitochondria to oligomerize and facilitate cytochrome c release, triggering caspase cascades.
BAX antibodies are widely used to detect BAX expression, localization, and activation status in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. They help elucidate BAX's role in diseases, particularly cancer, where dysregulated apoptosis contributes to tumor progression or chemoresistance. Specific antibodies may target distinct BAX epitopes, such as the N-terminus (inactive conformation) or exposed regions in activated BAX, enabling differentiation between its pro-apoptotic and dormant states.
Commercial BAX antibodies vary in host species, clonal specificity (e.g., monoclonal clones like 2D2 or polyclonal preparations), and validation across experimental models. Researchers must validate antibody specificity using controls like BAX-knockout cells, as cross-reactivity with related proteins (e.g., BAK) can occur. Recent studies also employ BAX antibodies to investigate non-apoptotic functions, including mitochondrial dynamics and cellular stress responses. Proper antibody selection ensures accurate interpretation of BAX's complex roles in health and disease.
×