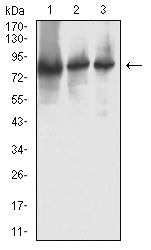
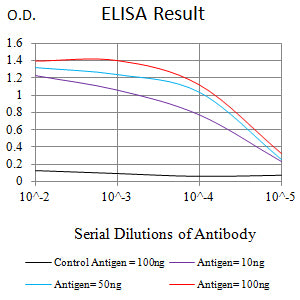
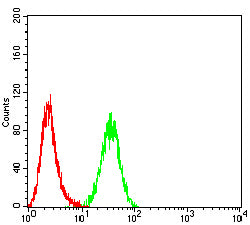
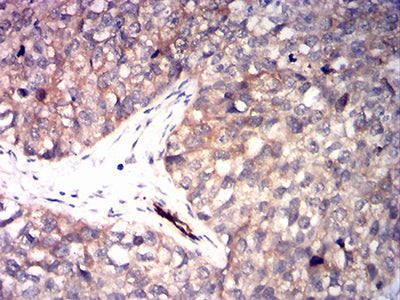
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | R1; RR1; RIR1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6240 |
| clone | 2D6D8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 90kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RRM1 (AA: 541-792) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与RRM1抗体相关的文献及其摘要概括(信息基于公开研究整理,具体内容请参考原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"RRM1 expression and efficacy of gemcitabine in patients with non-small cell lung cancer"*
**作者**: Zheng Z, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组化(IHC)检测非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)组织中RRM1蛋白表达水平,发现高RRM1表达与患者对吉西他滨化疗耐药性显著相关,提示RRM1抗体可作为预测化疗反应的生物标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Validation of RRM1 antibody for immunohistochemical analysis of breast cancer subtypes"*
**作者**: Davidson B, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了多种RRM1抗体在乳腺癌组织中的特异性,发现克隆号15A9的抗体在区分三阴性乳腺癌亚型中表现最佳,且RRM1高表达与患者生存期缩短相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"RRM1 as a prognostic marker in gastric cancer: A multi-center study using tissue microarray"*
**作者**: Kim HS, et al.
**摘要**: 通过组织芯片结合RRM1抗体(克隆号EPR3956)分析胃癌样本,发现RRM1过表达与肿瘤侵袭性及患者总生存率降低显著相关,支持其在胃癌预后评估中的价值。
---
如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索标题或作者名获取全文。
The RRM1 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the ribonucleotide reductase catalytic subunit M1 (RRM1), a key enzyme in DNA synthesis and repair. Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) catalyzes the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides, essential for DNA replication and cell proliferation. The RNR holoenzyme consists of two subunits: RRM1. which harbors the catalytic site and allosteric regulatory sites, and RRM2 (or p53R2 in stress conditions), which provides a stable radical for catalysis. RRM1 expression is tightly regulated during the cell cycle and is often elevated in rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells.
RRM1 antibodies are widely used in biomedical research to detect RRM1 protein levels in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. These antibodies help investigate RRM1's role in cancer progression, chemoresistance (e.g., resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic or lung cancer), and its potential as a prognostic biomarker. Overexpression of RRM1 has been linked to poor survival in cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), while low RRM1 levels may predict better response to antimetabolite therapies. Researchers also utilize RRM1 antibodies to explore its interplay with oncogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targeting strategies. Validation of antibody specificity remains critical, as cross-reactivity with homologous proteins can affect data interpretation.
×