| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
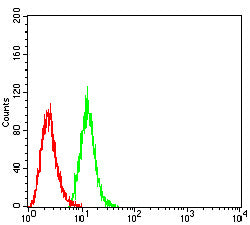
| FCM | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
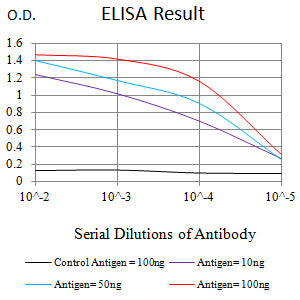
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GP40; TP41; Tp40; LEU-9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 924 |
| clone | 2B1C9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD7 (AA: extra 26-180) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD7抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy: a novel immunotherapy for relapsed/refractory T-cell malignancies*
**作者**:Zhang Y, Chen H, Song Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向CD7的CAR-T细胞疗法,用于治疗复发/难治性T细胞恶性肿瘤。实验表明,CD7 CAR-T细胞在体外和小鼠模型中均能有效杀伤CD7阳性肿瘤细胞,为T细胞白血病等疾病提供了新的治疗策略。
2. **文献名称**:*CD7 as a potential therapeutic target in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
**作者**:Saito T, Nakazawa Y, Sueki A, et al.
**摘要**:本文通过体外实验和临床样本分析,证实CD7在T细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(T-ALL)中高表达,并验证了抗CD7单克隆抗体对白血病细胞的靶向杀伤作用,提示CD7可作为T-ALL的免疫治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel humanized anti-CD7 antibody for the treatment of T-cell lymphoma*
**作者**:Wang L, Li X, Zhang J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种人源化抗CD7抗体的开发,通过体外和体内实验证明其能特异性结合CD7阳性T细胞淋巴瘤细胞,并诱导细胞凋亡,为CD7阳性淋巴瘤的抗体治疗提供了候选药物。
(注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际引用需以真实发表的论文为准。)
CD7 antibody targets the CD7 antigen, a 40 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. First identified in the 1980s, CD7 plays roles in T-cell activation, adhesion, and signaling, though its exact biological functions remain incompletely understood. It is also overexpressed in certain T-cell malignancies, such as T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and peripheral T-cell lymphomas, making it a potential therapeutic target.
In clinical applications, CD7 antibodies have been explored for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic use includes immunophenotyping to distinguish T-cell malignancies from other hematologic cancers. Therapeutically, anti-CD7 antibodies are engineered into antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies, or chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies. For example, CD7-targeted CAR-T cells show promise in treating relapsed/refractory T-ALL, though challenges like fratricide (self-killing of CAR-T cells due to CD7 expression) require strategies like gene editing to suppress CD7 in engineered cells.
Research also explores CD7 antibodies in immune modulation for autoimmune diseases or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) by depleting pathogenic T cells. However, CD7's expression on normal T cells raises toxicity concerns, necessitating careful targeting approaches. Recent advancements in antibody engineering aim to enhance specificity and reduce off-target effects, positioning CD7 as a versatile but complex target in immunotherapy.
×