| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
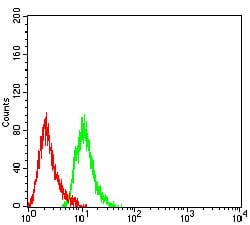
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
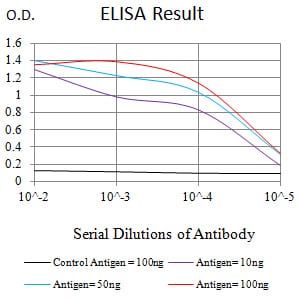
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LIR; CLM-6; CMRF35; IGSF16; CMRF-35; CMRF35A; CMRF-35A; CMRF35A1; CMRF35-A1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10871 |
| clone | 5E1H8A5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD300C (AA: 21-183) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD300C抗体的3篇文献参考(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*CD300C regulates myeloid cell differentiation and inflammatory responses*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究CD300C抗体在髓系细胞中的功能,揭示其通过调控TLR信号通路影响炎症反应,并可能作为自身免疫疾病的治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural characterization of CD300C and its role in platelet activation*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析CD300C胞外结构域,并利用抗体阻断实验证明其在血小板活化和血栓形成中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*CD300C antibody-based targeting suppresses tumor growth in murine models*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:开发靶向CD300C的单克隆抗体,在肿瘤微环境中通过调节巨噬细胞极化抑制肿瘤生长,提示其抗肿瘤免疫治疗潜力。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索。)
CD300c antibody targets the CD300c protein, a member of the CD300 family of immunoregulatory transmembrane receptors. These receptors play critical roles in modulating immune responses by recognizing lipid-based ligands, such as phosphatidylserine exposed on apoptotic cells or pathogens. CD300c, also known as CD300LB, is primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, dendritic cells, and neutrophils. It functions as an activating receptor, promoting pro-inflammatory signaling through its association with adaptor proteins like DAP12 or FcRγ, which contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs). This activation can enhance phagocytosis, cytokine production, and pathogen clearance.
Research on CD300c antibodies focuses on understanding its role in immune regulation and disease contexts. Dysregulation of CD300 family members has been linked to inflammatory disorders, infections, and cancer. CD300c-specific antibodies are valuable tools for detecting receptor expression, blocking ligand interactions, or modulating immune cell activity in experimental models. For instance, studies suggest CD300c may influence sepsis outcomes by regulating neutrophil responses or contribute to tumor evasion by altering myeloid cell function. Developing therapeutic antibodies targeting CD300c could offer strategies to fine-tune immune activation in conditions like autoimmune diseases or cancer immunotherapy. However, its precise ligand specificity and signaling crosstalk with other receptors remain areas of active investigation.
×