| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
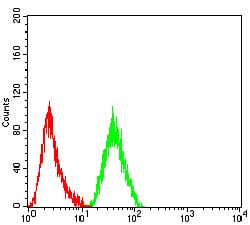
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
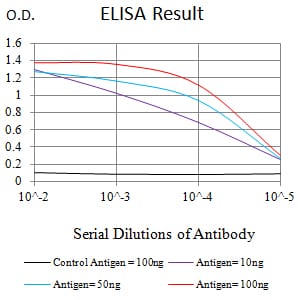
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | L1CAM; S10; HSAS; MASA; MIC5; SPG1; CAML1; HSAS1; N-CAML1; NCAM-L1; N-CAM-L1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3897 |
| clone | 5C6A10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 140kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD171 (AA: 20-197) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD171(L1CAM)抗体相关的研究文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟概括,具体引用请核实原始论文):
---
1. **文献名称**: "CD171-directed CAR T cells exhibit anti-tumor activity in neuroblastoma models"
**作者**: Mueller KT, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了靶向CD171的CAR-T细胞,并在神经母细胞瘤小鼠模型中验证其疗效。结果显示,CD171抗体修饰的CAR-T能特异性识别并杀伤肿瘤细胞,显著抑制肿瘤生长,提示其在免疫治疗中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: "L1CAM antibody blockade suppresses metastasis in colorectal cancer by disrupting tumor-stroma interactions"
**作者**: Svensson A, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨了抗CD171/L1CAM抗体对结直肠癌转移的抑制作用。研究发现,抗体通过阻断L1CAM与肿瘤微环境中基质细胞的互作,降低癌细胞侵袭能力,并抑制EMT过程,为抗转移治疗提供新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Structural characterization of L1CAM epitopes using monoclonal antibodies reveals functional domains"
**作者**: Schäfer MK, et al.
**摘要**: 利用多种抗CD171单克隆抗体解析L1CAM蛋白的功能结构域,发现特定表位抗体可干扰细胞粘附和信号传导,为开发靶向L1CAM的诊断工具或治疗药物奠定分子基础。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD171 antibody”“L1CAM therapeutic”等获取最新研究。
CD171. also known as L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It plays critical roles in neural development, including axon guidance, neuronal migration, and synaptic plasticity, mediated through homophilic and heterophilic interactions. Beyond the nervous system, CD171 is aberrantly expressed in various cancers, such as neuroblastoma, melanoma, and ovarian carcinoma, where it promotes tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance by enhancing cell adhesion, survival, and invasion.
CD171 antibodies are tools developed to target this molecule for research and therapeutic purposes. In research, they are widely used in immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and functional studies to explore CD171's biological roles and its association with malignancies. Therapeutically, anti-CD171 antibodies have been investigated as potential agents for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or immunotherapies, leveraging their ability to specifically bind cancer cells expressing CD171. For instance, preclinical studies in neuroblastoma have shown promising results by delivering cytotoxic payloads directly to CD171-positive tumor cells.
Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity to minimize off-target effects and overcoming variable CD171 expression across tumor subtypes. Despite this, CD171 remains a compelling target due to its restricted normal tissue expression and strong link to aggressive cancer phenotypes. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody engineering and explore combinatorial therapies to enhance clinical efficacy.
×