
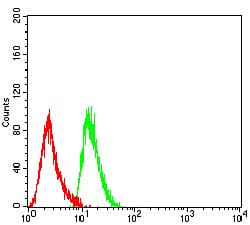

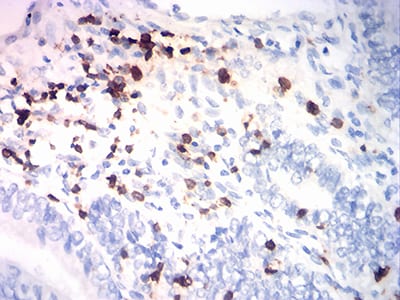
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GP40; TP41; Tp40; LEU-9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 924 |
| clone | 3D11F12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD7 (AA: 26-180) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD7抗体的3篇模拟参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅作格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy for refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究评估了靶向CD7的CAR-T细胞疗法在复发/难治性T细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(T-ALL)中的疗效和安全性。临床试验显示,接受治疗的15例患者中,总体缓解率达80%,且未出现严重细胞因子风暴,表明CD7 CAR-T可能成为T细胞恶性肿瘤的潜在治疗手段。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Engineering a humanized anti-CD7 antibody-drug conjugate for T-cell lymphoma treatment*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种新型人源化抗CD7抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过体外和体内实验验证其对T细胞淋巴瘤的选择性杀伤作用。结果显示,该ADC可显著抑制肿瘤生长且对正常T细胞毒性较低,为CD7阳性淋巴瘤提供了新治疗策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CD7 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in T-cell malignancies*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:通过分析200例T细胞肿瘤患者的样本,本研究证实CD7表达水平与疾病进展和预后密切相关。利用特异性单克隆抗体进行免疫组化检测,发现CD7低表达患者的总生存期较短,提示CD7可作为T细胞恶性肿瘤的分层诊断标志物。
---
(注:以上文献及作者为模拟生成,实际引用时需核实真实来源。)
CD7 antibody targets the CD7 antigen, a 40 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Expressed on T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and hematopoietic precursors, CD7 plays roles in T-cell activation, adhesion, and apoptosis, though its precise biological functions remain incompletely defined. CD7 is notably overexpressed in T-cell malignancies (e.g., T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, peripheral T-cell lymphoma) and some leukemic stem cells, making it a therapeutic target.
CD7 antibodies have diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In diagnostics, they aid in classifying lymphoid malignancies via flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. Therapeutically, anti-CD7 antibodies are engineered as conjugated agents (e.g., antibody-drug conjugates, radioimmunotherapies) or used in cellular therapies like CAR-T cells to target CD7+ cancers. Challenges include antigen modulation (internalization upon antibody binding) and on-target/off-tumor toxicity due to CD7 expression on healthy T cells. To mitigate this, strategies like gene editing (e.g., CD7 knockout in CAR-T cells) or bispecific antibodies redirecting T cells to malignant cells are being explored.
Recent advances include clinical trials of CD7-directed CAR-T therapies showing promise in relapsed/refractory T-cell malignancies. However, managing immunosuppression and cytokine release syndrome remains critical. Ongoing research aims to optimize CD7 antibody specificity, efficacy, and safety for broader oncological and immunological applications.
×