
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
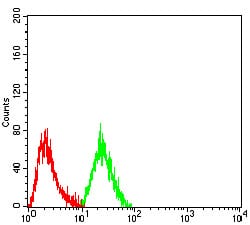
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
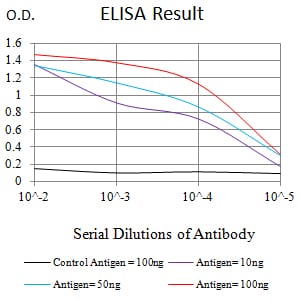
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARF; MLM; P14; P16; P19; CMM2; INK4; MTS1; TP16; CDK4I; CDKN2; INK4A; MTS-1; P14ARF; P19ARF; P16INK4; P16INK4A; P16-INK4A |
| Entrez GeneID | 1029 |
| clone | 4A10E1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 16.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CDKN2A/P16 (AA: 1-156) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CDKN2A/P16抗体的代表性文献(名称、作者及摘要内容概括):
1. **《p16INK4a immunohistochemistry improves interobserver agreement in the diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia》**
- **作者**:Alla Lázár 等
- **摘要**:该研究验证了p16抗体在宫颈活检组织中的诊断价值,证明其过表达与高危HPV感染相关,能显著提高宫颈上皮内瘤变(CIN)病理诊断的一致性,辅助鉴别反应性增生与癌前病变。
2. **《Immunohistochemical expression of p16 in melanocytic lesions》**
- **作者**:David E. Elder 等
- **摘要**:通过免疫组化分析p16在良恶性黑色素瘤中的表达差异,发现p16缺失与侵袭性黑色素瘤显著相关,提出p16抗体可作为辅助诊断黑色素瘤恶性程度的生物标志物。
3. **《p16 expression correlates with survival in carcinomas of the anterior tongue》**
- **作者**:Angelo G. Giordano 等
- **摘要**:研究舌前部鳞癌患者的p16蛋白表达水平,发现p16高表达与HPV阳性肿瘤及患者较长总生存期相关,提示p16抗体检测可用于预后评估及治疗策略制定。
4. **《Role of p16 in the pathogenesis of melanoma》**
- **作者**:Michael S. Sabel 等
- **摘要**:探讨CDKN2A/p16基因缺失在黑色素瘤发生中的作用,通过Western blot和免疫组化证实p16蛋白缺失导致细胞周期失控,强调p16抗体在分子机制研究中的关键作用。
The CDKN2A gene, located on chromosome 9p21. encodes the p16 protein, a critical tumor suppressor involved in cell cycle regulation. P16 inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6), preventing phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein and arresting the cell cycle at the G1 phase. Loss of p16 function, through deletions, mutations, or promoter methylation, disrupts this checkpoint, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation—a hallmark of cancer. CDKN2A/p16 alterations are frequently observed in cancers such as melanoma, pancreatic, and lung carcinomas, making it a key biomarker for tumorigenesis and prognosis.
Antibodies targeting p16 are widely used in research and diagnostics to assess protein expression via immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, or immunofluorescence. In clinical pathology, p16 overexpression is often a surrogate marker for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in cervical and head/neck cancers, where viral oncoproteins E6/E7 dysregulate Rb, leading to compensatory p16 upregulation. However, interpretation requires context: some cancers show p16 loss (e.g., gliomas), while others exhibit gain (e.g., HPV-associated tumors). Discrepancies in antibody specificity, epitope recognition, and staining protocols can affect reproducibility, emphasizing the need for validated reagents and standardized methods. Overall, p16 antibodies remain vital tools for understanding cell cycle dysregulation and guiding cancer diagnostics.
×